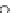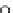Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Extracellular Space
Dendritic Spine
Lipid Membrane
Nucleus
Axon Hillock
Legs Kinesin
Synaptic terminal
Presynapse
Synaptic cleft
Vesicle
Postsynapse
Figure 1.1:
Schematic of a typical neuron.
Haptin (to fasten). There are approximately 10
15
synapses in the brain, so each neuron has on average
1,000 synapses.The number of synapses in an individual neuron, however, can vary greatly. It is important
to note that the synapse is not a singular structure, but rather the combination of three structures. The
pre-synapse
is the very end of an axon and houses
vesicles
, or small spheres of membrane, that contain
neurotransmitters
. The
post-synapse
is on the very end of a dendrite. The 20
nm
space between the pre-
synapse and post-synapse is called the
synaptic cleft
and is technically outside of both neurons.
Neurotransmitters are specializedmolecules that are packaged into vesicles in the soma, transported
to the end of the pre-synaptic axon by the legs kinesin, and released into the synaptic cleft in response
to an electric impulse. Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic cleft and reach the post-synapse
where they either excite or inhibit electrical impulses in the dendrite of a new neuron. There is enormous
diversity in the molecules that function as neurotransmitters as well as the mechanisms by which they
affect the post-synapse.