Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
scalp. The deflections, although in the
μV
range, correlate to the activity of the brain in regions under
the electrode. Therefore, the EEG is typically recorded using many electrodes positioned directly above
known brain structures.
8.3
PRACTICAL ASPECTS OF RECORDING NEURAL
POTENTIALS
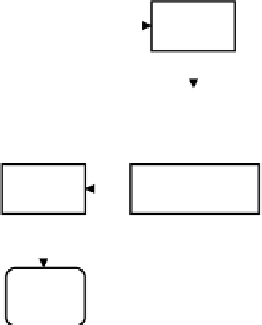
The typical process of recording and storing electric potentials is summarized in Fig. 8.3. In the section
below, we review the key components of a recording system. Processing will be the subject of Ch. 9.
Signal
Preamp
Electrode
Analog
Filter
Amp
Digital
Filter
A/D
Processing
Display
Figure 8.3:
Recording, filtering, amplification, and digitization of an extracellular potential.
8.3.1 Electrodes
Currents in the brain are carried by ions. Currents in computers and wires, however, are carried by
electrons. The role of an electrode is therefore to transduce ionic current to electric current. The chemical
reaction most typically used is:
Ag
+
+
e
−
Ag
Ag
+
+
Cl
−
AgCl .
Although many metals could be used to create an electrode, the
Silver-Silver Chloride
electrode is easy to
fabricate, has a fast electrical response, and is compatible with biological tissues.
Electrodes for recording potentials from tissue are typically small (
<
1
mm
). They can be placed
directly on the surface of neural tissue or, since neural tissue is somewhat spongy, can easily be pushed
deep inside of a three-dimensional section of tissue. Recordings made in the brain are typically called
cortical recordings
if the electrodes are one the surface of the brain, or
sub-cortical
if they are pushed into