Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
20
16
Rainfall
(inches)
12
Dust Bowl Drought
(1928-1935)
8
1977 Drought
4
1870 1910 1950 1990 2007
Year
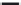
f igu r e 7. Precipitation during winter (November through April) from 373 stations in
the western United States from 1871 to 2007. h e year 1976-77 was the driest on record
(including paleoclimate records from the past 500 years). (Graph courtesy of Dr. James
Johnstone at the Joint Institute for the Study of the Atmosphere and Ocean, University of
Washington.)
increased from 40 percent of the total amount of water consumed during
a normal year to 53 percent, causing a precipitous drop in the water table
throughout California. Particularly hard-hit was the southern Central Valley
(the San Joaquin Valley), where the water table dropped so low (by up to i t y
feet) that pumping capability could not keep up with demand from irrigated
agriculture, and groundwater depletion was estimated to be i ve million
acre-feet, or four times the annual average. Nine thousand water wells were
deepened or drilled. In order to aid in water ei ciency, many farmers shit ed
from growing rice and other water-intensive crops to grains, particularly
barley, wheat, and oats.
Well over seven and a half million trees died as a result of the 1976-77
drought. Some regions in the highest elevations of the Sierra Nevada lost
three-fourths of their trees, including ponderosa and Jef rey pines, red i rs,
and white i rs. h ese trees, weakened by the lack of water, succumbed to
insect-related diseases like bark beetle or to longer-term conditions such as
mistletoe and root rot. Wildi res also claimed many trees. In August 1977