Java Reference
In-Depth Information
Using the Command Prompt Window
This appendix describes how to open the Command Prompt window and then set properties to define
how the Command Prompt window displays. It also discusses how to change to the proper drive and
directory. Finally, it covers how to set the environmental variables in order to compile and run a sam-
ple program found on the Data Disk that accompanies this topic.
Opening and Setting Properties of the Command Prompt Window
In Windows, the
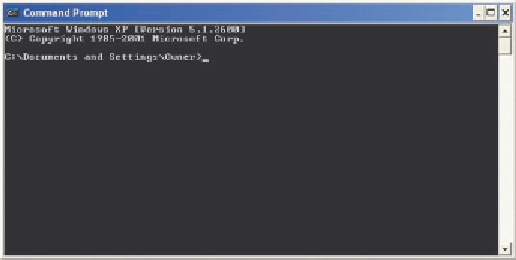
Command Prompt window
(Figure D-1) is a way to communicate with the
operating system and issue commands without using a program with a graphical user interface. Most
versions of Windows contain a Command Prompt command on the Accessories submenu, which
allows you to open a Command Prompt window. Opening a Command Prompt window on the desk-
top facilitates moving between editing programs and running them.
Command
Prompt window
insertion
point
command
prompt
FIGURE D-1
As shown in Figure D-1, the Command Prompt window displays a
command prompt
that
includes a disk drive location, followed by a subdirectory location (if any), followed by a greater-than
sign (>), and finally a flashing insertion point. The insertion point designates the place where users
type commands and enter responses.
The Command Prompt window normally displays light gray text on a black screen, with a default
font size of 8
×
12 pixels or a similar size. In order to make the screens easier to read in this topic, the
Command Prompt window properties were set to use a font color of white and a font size of 12
×
16
pixels. The following steps open the Command Prompt window and set its properties to match the
figures in this topic.








Search WWH ::

Custom Search