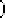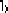Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 1.18:
(a) Result of registration of data in Figs. 1.16.a and 1.16.b. (b)
Result of registration of data in Figs. 1.16.a and 1.16.c.
The Jewish Hospital Foundation in Louisville, KY., proposed a cancer screen-
ing and early detection study in a randomized trial with the following specific
aims: (1) to determine whether the use of spiral CT scanning of the chest detects
early lung abnormalities that lead to cancer, which are not visible on chest X-rays
in patients at high-risk for developing lung cancer; and (2) to determine whether
annual spiral chest CT scans of the chest in high-risk patients result in an im-
provement in survival. To test and prove these hypothesis, data was collected
from 1000 symptomatic patients above 60 years of age with positive smoking
history will undergo screening with low dose spiral CT (LDCT) and chest ra-
diography. Screening was performed every three months on the selected 1000
symptomatic patients. The role of the image registration process was to help in
studying the development of abnormalities.
Again, maximization of mutual information enhanced by using genetic algo-
rithms was used in this application. Figure 1.16 shows different CT images for
the same patient taken at various periods. Registration of these images using
the mutual information criterion was performed fully automatically on a PC
computer with microprocessor 2.4 GHz. The algorithm took less than 8 min.
to register all data. The recovered rotational transformation parameters were
generally smaller than 15 degrees, while the translational parameters varied up
to 20 mm. Figure 1.17 shows how the GA iterations improve the MI measure
overtime until maximum fitness is reached. Figure 1.18 shows the results of