Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
A
B
1.01
0.93
C
D
C
D
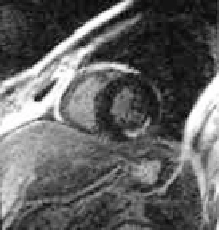
Figure 12.15: (A) Mid-ventricle contrast-enhanced MRI image of the left ven-
tricle. The hyperenhancement indicates the location of the infarction (arrow
in left panel). (B) Circumferential stretch distribution for systolic contraction.
The arrow indicates the infarcted area of the lateral wall does not contract dur-
ing systole. Mid-ventricle slices of the 3-D cine MRI image data used for the
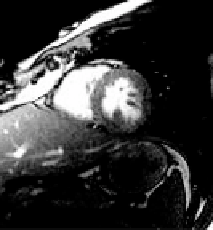
systolic function analysis. (C) Mid-systolic image (
template
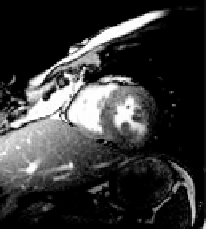
). (D) End-systolic
image (
target
).
end-diastole was designated the
target
image (Fig. 12.15D). A warping model
and analysis was made using the methods detailed above.
The warping analysis reveals that the infarcted area undergoes little defor-
mation during systole (circumferential stretch near 1.0). The analysis further re-
veals that the wall dysfunction extends over the lateral wall of the myocardium
outside the area of hyperenhancement indicated in the ce-MRI images (Fig.
3.15A). These results indicate that the contractile function of the heart is signifi-
cantly impaired within and adjacent to the infarcted region.
12.4
Discussion and Conclusions
Hyperelastic Warping is a highly flexible registration method that can be used
for the registration of physical and nonphysical deformations. It makes use of