Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Malleus Surface Definition
Warping Displacement Magnitude
µ
m
A
B
120
0
Effective Stress MPa
Surface Displacement Magnitude
µ
m
C
D
1800
120
0
0
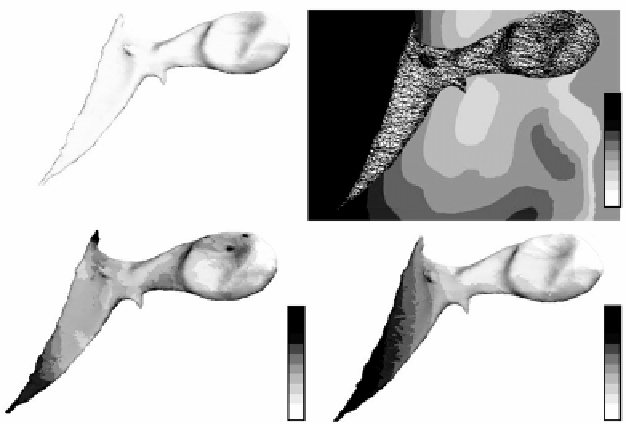
Figure 12.8:
(A) Rendered surface definition of the gerbil malleus. (B) Displace-
ment magnitude warping results for a plane bisecting the center of the malleus.
The tetrahedral mesh has been superimposed on the results to indicate the lo-
cation of the malleus within the displacement field. (C) Effective stress and (D)
displacement magnitude results for the surface of the malleus.
stress/strain distribution within the bone using only the surface displacements
as the boundary conditions.
The results indicate that the manubrium, which is at the center of tympanic
membrane, undergoes the greatest displacement and is a high stress region of
the malleus (Figs. 12.8C and 12.8D). In contrast, the head of the malleus, which
has attachments to the head of the incus and the superior ligament, shows the
least displacement and is a low stress region. These results suggest that the
malleus acts to decrease the energy being transferred to the incus. Further, this
analysis demonstrates how the deformation map from a deformable image reg-
istration analysis using Hyperelastic Warping can be integrated into a traditional
computational biomechanics analysis using the FE method.
12.3.3
Strain Measurement of the Coronary Artery
using Intravascular Ultrasound
Coronary heart disease is currently the leading cause of death in the United
States [47]. Plaque rupture, the structural failure of the plaque cap, is the primary