Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
r-medLip
l-medLip
l-medColl
r-medBR
l-medBR
r-medColl
r-latLip
l-latLip
r-latColl
l-latBR
r-latBR
l-latColl
l-vMB
r-vMB
CB
PL-SOG
l-Lob
r-Lob
r-Med
l-Med
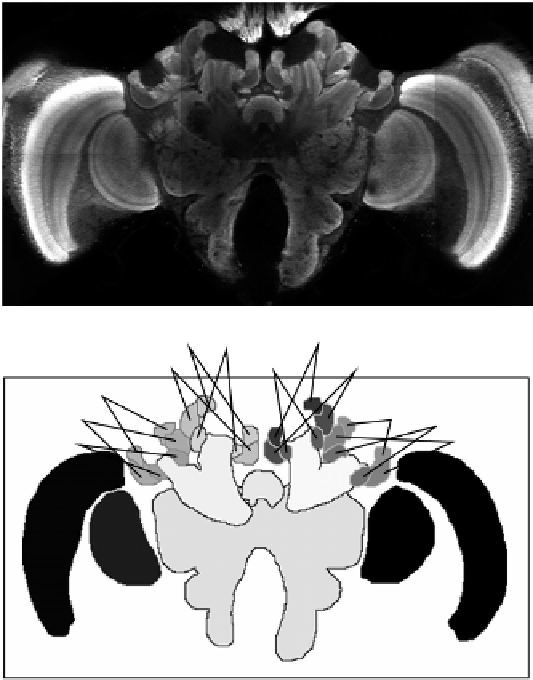
Figure 11.1: Example of bee brain confocal microscopy (
top
) and correspond-
ing label image as defined by manual segmentation (
bottom
). Following radio-
logical convention for axial slices, the image is seen from the cranial direction.
Every gray level in the label image represents a different anatomical structure.
Due to limitations of reproduction different gray levels may look alike. The
correspondence between anatomical structures and abbreviations is listed in
Table 11.1. Note that two structures, the left and right antennal lobes (
l-AL
and
r-AL
), are not visible in this slice, but can be seen in Fig. 11.2.
11.3
Fundamentals of Atlas-Based
Segmentation
n
Mathematically
→
from
n
-
dimensional spatial coordinates to labels from a set of classes
.Itis
speaking,
an
atlas
A
is
a
mapping
A
:
R