Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Floating Image
Initial Transform
Transform
Update Transform
Reference Image
Transformed Floating
No
CE/RCE/SD
Optimal
(min/max)?
Compute
CE/RCE/SD
Yes
Final Transform
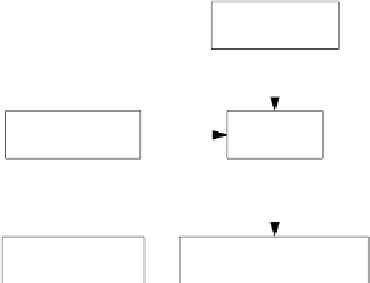
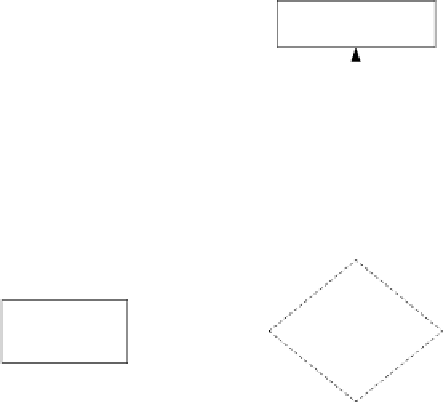
Figure 10.1: Flow chart of image registration by the cross-entropy, reversed
cross-entropy, and symmetric divergence optimization. CE: cross-entropy; RCE:
reversed cross-entropy; SD: symmetric divergence.
The two images involved in the registration are identified as the reference
image and the floating image. The floating image will undergo rotation and trans-
lation to match the reference image. Before the automatic registration starts,
an initial set of registration parameters must be set and the floating image is ap-
propriately transformed (i.e., rotated and translated). The similarity measures
between the reference image and the transformed floating image are then com-
puted. If the similarity number is not optimal, the registration parameters are
updated, otherwise, the registration process stops and the optimal registration
parameters are output. The scheme to update the registration parameters is de-
termined by the optimization algorithm employed. In the following subsections,
the key steps in the registration process are expanded and discussed in detail.