Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Global affine registration
Quadratic multigrid registration
Robust multigrid registration
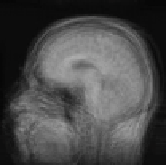
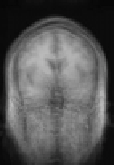
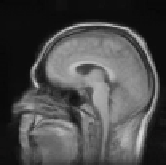
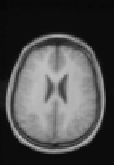
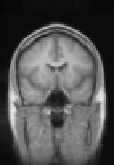
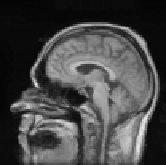
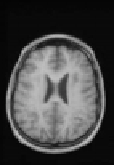
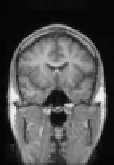
Figure 8.18: Results of experiments on a database of 18 subjects. One sub-
ject was chosen as the reference subject (see Fig. 8.19), and we averaged all
the reconstructed volumes after global affine registration (top), after quadratic
multigrid registration (middle) and after robust multigrid registration (bottom).
We kept the same set of parameters for all the subjects. This demonstrates the ro-
bustness of the method, and the importance of robust estimators (the quadratic
registration is less accurate on the cortex).
section 8.3.3, we evaluate in this section the registration process by computing
the overlap between the tissues (gray matter and white matter) of the reference
volumes and the tissues of each studied volume after registration. We measure
the overlap with the total performance, which has already been presented in
section 8.3.3.
The extraction of gray matter and white matter is performed using a tech-
nique presented in [85]. It consists in a 3D texture analysis to compute statis-
tical attributes of each voxel. A clustering procedure is used to find the ini-
tial discrimination of the data, and a bayesian relaxation refines the primary
decision.