Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
intensity distribution; and variations in intensities of tissues surrounding the
brain. Since an error-proof image segmentation method cannot be developed,
user assistance is needed to correct the obtained errors. At present, the best
one can hope for is to have a segmentation method that can correctly find most
areas of an object of interest, and in areas where it makes a mistake, allow the
user to correct them.
We have developed a computer-aided design system that allows a user to
revise the result of an automatically determined segmentation. We assume the
region obtained by an automatic method has a spherical topology. We also as-
sume the region represents voxels forming the bounding surface of an object of
interest in a volumetric image. The developed system fits a parametric surface
to the voxels and overlays the surface with the volumetric image. By viewing
both the image and the surface, the surface is edited until the desired shape is
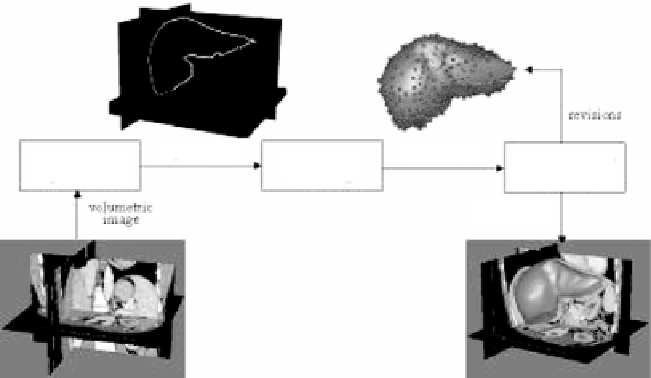
obtained. The idea behind the proposed method is depicted in Fig. 7.1.
Various user-guided and interactive segmentation methods have been devel-
oped. Barrett, Falc ao, Udupa, Mortensen, and others [1, 8, 21, 22, 26] describe
revisions
digital shape
Automatic
Segmentation
surface model
ROI
Modeling
3-D interactive
Editing
volumetric
image
segmentation
result
Figure 7.1:
The computer-aided design system used in region editing. The sys-
tem starts with a region obtained from an automatic segmentation method.
It then represents the region by a free-form parametric surface and overlays
the surface with the volumetric image. The user then revises the surface while
viewing both the volumetric image and the surface. The final result is generated
parametrically or in digital form.