Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
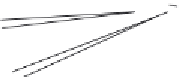
Figure 2.2 The arrestin-fold protein family tree. The sequences of mammalian arrestins
(ARR) and ARRDCs and yeast ARTs were blasted against the genome of C. elegans,
D. melanogaster, D. discoideum, C. intestinalis, Tetrahymena thermophila,andParamecium
tetraurelia. Alternately, the modeled structures of human b-arrestin 1 and yeast Aly1 were
searched against the genome of human and yeast, respectively, using the BackPhyre
option of the Phyre 2 (ProteinHomology/analogY Recognition Engine V 2. 0) web engine
71
in order to search for new proteins sharing the arrestin fold. The entire list of hits
(BlastþBackPhyre) was aligned using Clustal Omega
45
and a phylogenetic tree con-
structed with Splitstree 4 on the basis of this alignment.
72
The shown tree corresponds
to a Neighbor Joining tree, for which 1000 bootstrap steps were performed. All splits
supported by a bootstrap score above 95% were considered “correct”
73
and are shown
with a black dot. RGP1 homologs clustered with ART proteins (gray sector). The scale
bar shows the number of substitutions per site.
to phosphorylated GPCRs requires the displacement of InsP
6
. This step may
involve the binding of arrestins to phosphoinositides, the highest affinities
being observed for PtdIns(4,5)P
2
and PtdIns(3,4,5)P
3
. Phosphoinositides










































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search