Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Class A trafficking
Agonist
β
2
AR
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
Internalization
β
-Arrestin
P
Mdm2
Transient
ubiquitination
Transient
pERK
Endosome
C-Raf
ERK
MEK
β
-Arrestin
B
Class B trafficking
Agonist
AT
1a
R
V
2
R
P
P
P
P
P
P
Internalization
P
P
-Arrestin
P
E3 ligase?
Stable
ubiquitination
Sustained pERK;
formation of
signalsomes
Endosome
P
P
P
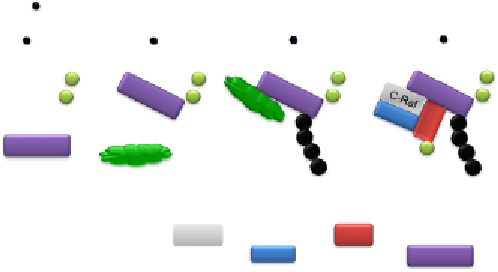
Figure 7.3 Ubiquitination and trafficking profiles of b-arrestin2. Agonist stimulation of
7TMRs leads to rapid phosphorylation of the receptor by GRKs. Phosphorylated recep-
tors recruit the cytosolic adaptor protein b-arrestin. Most 7TMRs are capable of rec-
ruiting b-arrestin. However, the nature of b-arrestin/7TMR complexes can be
transient (class A receptors) or stable (class B receptors). (A) Activation of the class
A b
2
adrenergic receptor (b
2
AR) induces rapid and transient ubiquitination of b-arrestin
by an E3 ubiquitin ligase, Mdm2. The ubiquitinated b-arrestin
-
receptor complex
engages an ERK-signaling scaffold at the plasma membrane and enhances transient
phosphorylation of ERK. The ubiquitinated b-arrestins are rapidly deubiquitinated
and dissociated from the internalizing receptor, while 7TMRs are internalized into
endocytic vesicles. (B) Activation of class B receptors induces sustained b-arrestin
ubiquitination by an unknown E3 ligase, leading to the formation of stable endocytic
complexes. These stable complexes are localized to perinuclear endosomal compart-
ments and ERK phosphorylation is sustained on signalsomes (signaling endosomes).















































































































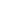

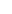






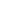
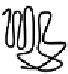
























































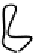














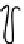




















Search WWH ::

Custom Search