Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Agonist
G protein-dependent
signaling
β
-Arrestin-dependent
signaling
α
β
γ
P
P
GRKs
Trafficking
Endocytosis
Degradation
Recycling
Effectors
Effectors
Second
messengers
Desensitization
Signal transduction
Signal transduction
Cell response
Cell response
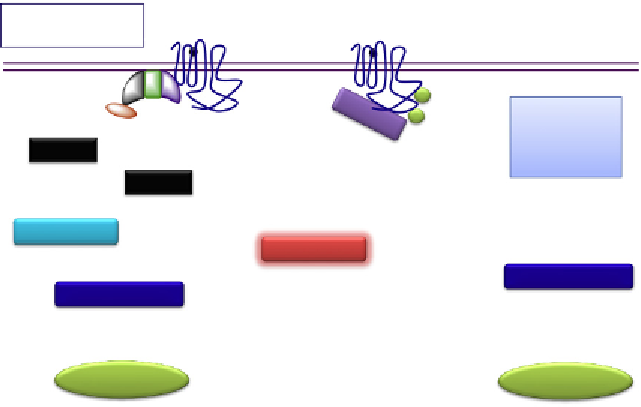
Figure 7.1 G protein and b-arrestin-dependent signaling elicited by 7TMRs. Agonist
binding to extracellular and/or transmembrane regions of the receptors leads to the
interaction and activation of heterotrimeric G proteins. The agonist-occupied 7TMR acts
as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF), catalyzing the exchange of GDP for GTP
on the G
a
subunit and inducing dissociation of the G
a
and G
bg
subunits from the com-
plex. The G protein subunits bind to enzymes or other effector molecules (e.g., ion chan-
nels) and modulate the levels of second messengers within the cell. This leads to the
activation of kinase cascades culminating in a cell response. G protein-dependent
signaling is terminated via 7TMR phosphorylation in the cytoplasmic domains by
G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs). Phosphorylated receptors bind b-arrestins
with high affinity. b-Arrestin recruitment from the cytosol to the phosphorylated recep-
tor at the plasma membrane leads to an immediate blockade of G protein coupling and
G protein-dependent signaling (desensitization); subsequently, b-arrestin interacts with
endocytic proteins such as clathrin and the clathrin adaptor protein 2 (AP2) and
facilitates 7TMR internalization and endocytosis. Additionally, b-arrestin bound to the
activated receptor can function as a signal transducer by initiating the b-arrestin-
dependent signaling pathway(s) by interacting and activating signaling kinases.
7TMRs from the plasma membrane into intracellular vesicles or endo-
somes.
13,14
b
-Arrestins were found to serve as adaptors for endocytic pro-
teins, first shown for clathrin, which is a structural component of
endocytic vesicles.
15-18
b
-Arrestins also bind to adaptin protein 2, which
functions together with clathrin for coat formation and transport of specific
cargo through the endocytic pathway.
19,20
The endocytic adaptor function
of
b
-arrestin is continually expanding to include new interacting proteins of
























Search WWH ::

Custom Search