Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
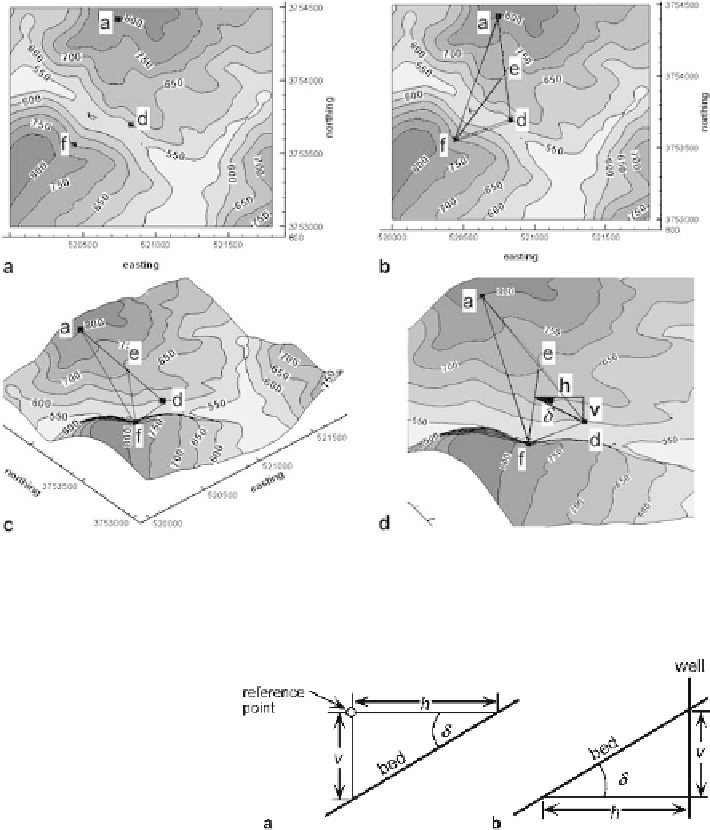
Fig. 2.20.
Attitude determination from three points on a topographic map. Horizontal scale in km, ver-
tical scale in ft.
a
Three points (
solid squares
) on a contact.
b
Determination of the strike line (e-f ).
c
The same three points in oblique 3-D view to NE.
d
Enlarged 3-D view of three-point solution
Fig. 2.21.
Distance to a point on a dip-
ping bed, in vertical cross
sections in the dip direction.
a
Vertical distance from a ref-
erence point to a dipping bed.
b
Horizontal distance from a
well to a dipping bed
A dip can be converted from degrees into feet/mile or meter/kilometer by solving Eq. 2.11
for
v
and letting
h
be the reference length (5 280 ft for ft/mile or 1 000 m for m/km):
v
=
h
tan
δ
,
(2.12)
where
v
= the vertical elevation change,
h
= reference length, and
= dip. The same
relationship can be used to determine the vertical distance from a reference point to
a dipping horizon seen in a nearby outcrop (Fig. 2.21a).
Another useful application of Eq. 2.11 is to find the distance to the intersection be-
tween a horizontal plane (such as an oil-water contact) and a dipping plane (such as
δ