Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
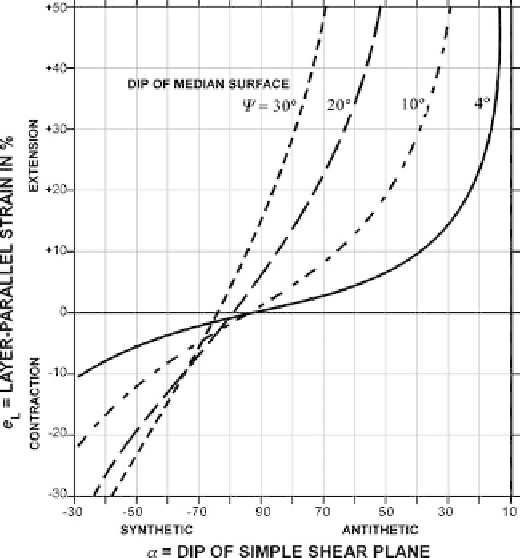
Fig. 11.51.
Layer-parallel strain in the
hangingwall of a normal fault
caused by simple shear oblique
to bedding for various angles
of dip of the median surface
of bedding (Eq. 11.14, after
Groshong 1990). All median
surface dips shown are toward
the master fault. Synthetic
shear dips in the same direc-
tion as the master fault and
antithetic shear dips opposite
to the master fault dip
deformation. Thus conjugate faults or domino blocks are expected (Sect. 1.6.4) with
orientations about 30° to
σ
1
is likely to be about normal to bedding, the
expected faults should have initial dips close to 60°, regardless of the shear angle that
connects the fault shape to the rollover geometry.
The structural styles that can be generated by small-scale faulting in a simple-shear
rollover are illustrated with a series of forward models. Assume that the deformation
mechanism in the rollover is the rotation of rigid dominoes with initial dips of 60°. The
final geometry is controlled by the relative amounts and directions of (1) the external
rotation of a median surface in the rollover, which is a function of the shear angle, and
(2) the domino rotation, which is a function of the amount of layer-parallel extension
(Sect. 11.5.2). The strain of the median surface is calculated from Eq. 11.14 and the
domino rotation, given the layer-parallel strain, from Eq. 11.38.
Domino blocks bounded by faults that are precisely antithetic to the master fault at
the beginning of deformation retain this geometry during extension (Fig. 11.52a). The
domino-block rotation is exactly canceled by the rotation of the rollover. Dominoes
that begin deformation with a steeper antithetic dip than the shear angle rotate away
from the master fault during deformation (Fig. 11.52b). The net rotation of the domino
blocks is relatively small. The geometries of Fig. 11.52a and 11.52b are common in the
East African Rift valleys (Rosendahl 1987), the North Sea (Beach 1986), the Gulf of
Suez (Colletta et al. 1988) and many other rifted environments. Dominoes that begin
deformation dipping the same direction but at a lower angle than the shear angle rotate
σ
1
. Because