Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
X
X
t
t
Forward Direction
Reverse Direction
Fig. 10.7
Vehicle detection signature
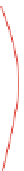
Sensor Displacement
Distance
Fig. 10.8
Vehicle direction sensing
further lower the voltage and decreasing concentration would raise the voltage, Fig.
10.7
[
28
]. For most applications, the amplitude and direction of voltage shift are not impor-
tant, but the detection of a significant shift in output voltage is of greater importance.
Vehicle direction sensing
. This method involves two sensors displaced at a small
distance apart, Fig.
10.8
[
30
]. The intention is that a vehicle in motion would create
the same signature, but displaced in time. The nearer sensor will hit the detection
threshold a fraction of a second before the front sensor in forward traffic. With a
known displacement distance and a reasonably precise time measurement between
thresholds detections, a speed computation can be made as well.
One of the biggest concerns for accurate vehicle detection system design is the
reception of false presence of vehicles (i.e., “falsing”). Even though vandals may toss
magnets onto the sensor areas and jeopardize the vehicle detection process, it is the nature
made stimuli or adjacent lane vehicles that comprise most of the falsing concerns.
10.5.2.2
Intra-vehicle Sensors
Most common representatives of the intra-vehicle sensors are the
speed
and the
distance
sensors. This subsection elaborates on them in greater details pinpointing
their most prominent characteristics.
















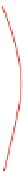




















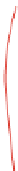










































Search WWH ::

Custom Search