Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
9.3.3
Lead Systems for Reconstructing 12-Lead ECG
Different dispositions of the electrodes from the reduced electrode sets have been
adopted [
14
]. Most of them are based on the assumption that a single, time-dependent
dipole can be used to represent the heart activity [
15
]. However, heart activity can
only be modeled accurately by several dipoles that change their spatial and time
states. Therefore, exact reconstruction of a measurement is, theoretically, not possible
with a smaller number of electrodes.
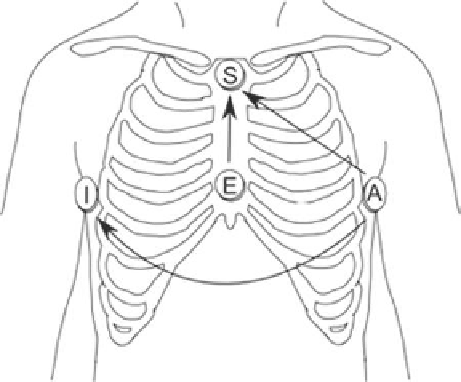
The EASI lead system [
2
] consists of four signal electrodes plus ground
electrode (Fig.
9.7
). The four recording sites result in three independent bipolar
measurements, E-S, A-S, and A-I. The 12-lead ECG is derived from a linear
combination of these three measurements, using optimized, fixed coefficients. The
locations of leads were chosen based on good anatomical landmarks allowing accu-
rate electrode location, good signal-to-noise ratio, and convenience for patients and
technicians.
As for most limited lead systems, the main advantage of the EASI system is that
the 12-lead ECG can be reconstructed from less than the ten recording electrodes
previously required. A further advantage is its reduced susceptibility to motion
artifacts, since the recording sites are located exclusively on the torso, away from
the extremities. Accurate positioning of the electrodes is also made easier, since
recording locations are at prominent anatomical landmarks. This is in contrast to
the precordial leads of the standard 12-lead ECG, which are often difficult to locate
accurately, particularly in women and children.
Nelwan et al. [
5
] investigated how well some absent precordial leads could be
reconstructed from the remaining leads of the standard 12-lead ECG. Sixty-three
different subsets of precordial leads were investigated with one or more leads
removed. For each subset, transformation coefficients were developed from which
Fig. 9.7
EASI lead
positioning
Search WWH ::

Custom Search