Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
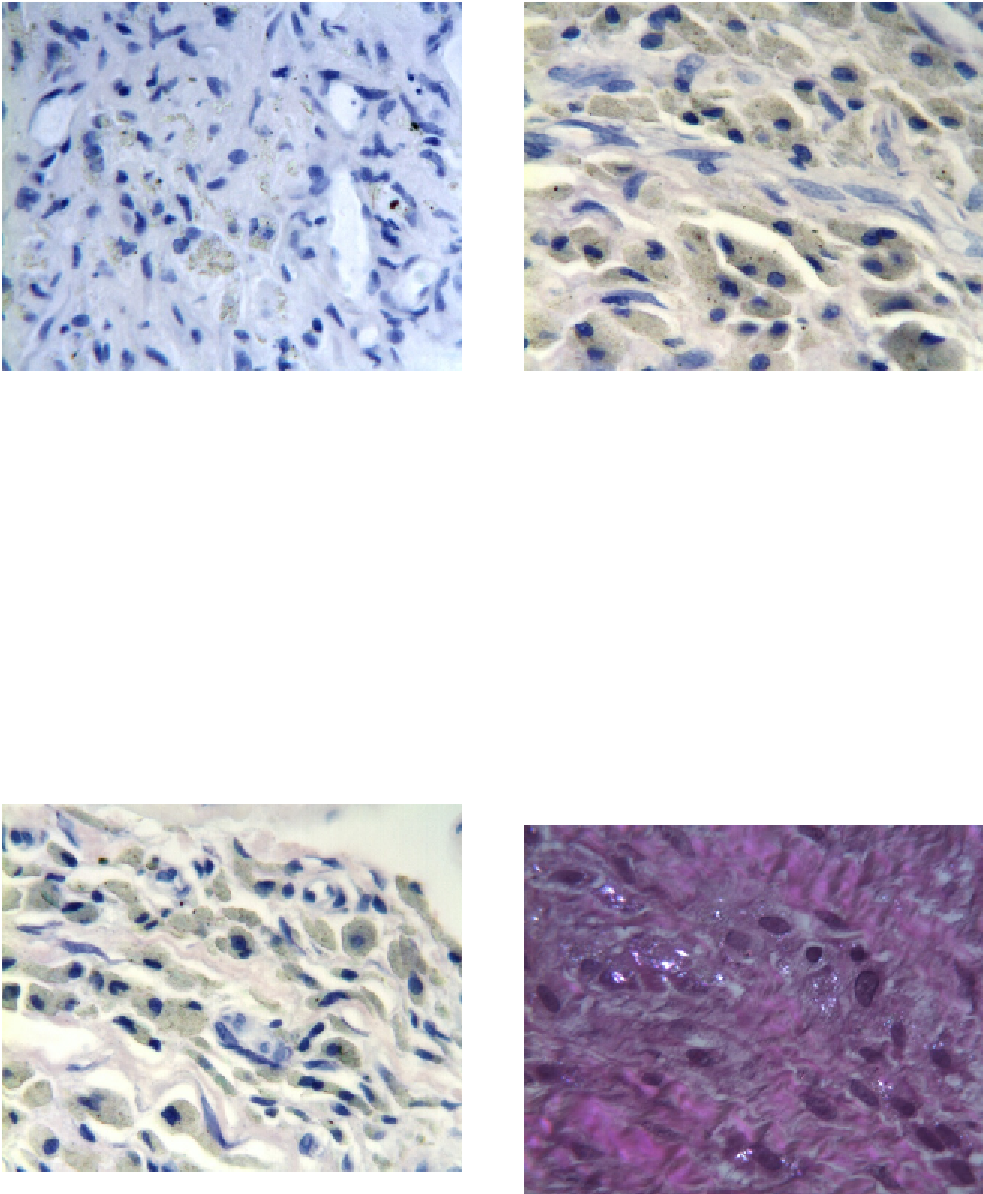
Figure 7.12
Periprosthetic tissues from an X-STOP
PEEK Interspinous Process Distraction (IPD) explant
showing a mononuclear response (macrophages
predominate) adjacent to intracellular and extracellular
PEEK particulate debris (WrighteGiemsa stain, original
magnification
Figure 7.14
Periprosthetic tissues from an X-STOP
PEEK Interspinous Process Distraction (IPD) explant
showing a multinuclear response (foreign body giant
cells predominate) with primarily intracellular PEEK
particulate debris
in fibrous
connective
tissues
500
).
(WrighteGiemsa stain, original magnification
500
).
¼
¼
greater than 50
m in diameter. There was no appre-
ciable host response to these larger particles. For the
majority of the explants, smaller intracellular PEEK
particulate debris was observed within macrophages
as well as fibroblasts. Intracellular PEEK particulate
debris was also observed within multinucleated
foreign body giant cells, but this was a less frequent
m
finding as the host response was primarily mono-
nuclear. Neutrophils, plasma cells, and eosinophils
were not observed in the histology of any of the
explants. By microscopic field, focal lymphocyte
infiltration was very infrequently observed in the
histology of a few of the patients. By the number of
microscopic fields, this was an infrequent finding.
Figure 7.13
Periprosthetic tissues from an X-STOP
PEEK Interspinous Process Distraction (IPD) explant
showing a mononuclear response (macrophages
predominate) with primarily intracellular PEEK particu-
late debris in fibrous connective tissues (WrighteGiemsa
Stain, original magnification
Figure 7.15
Periprosthetic tissues from an X-STOP
PEEK Interspinous Process Distraction (IPD) explant
showing birefringent polymeric debris in the tissue
sample received with the device (H&E stain, partially
polarized light, original magnification
500
).
500
).
¼
¼