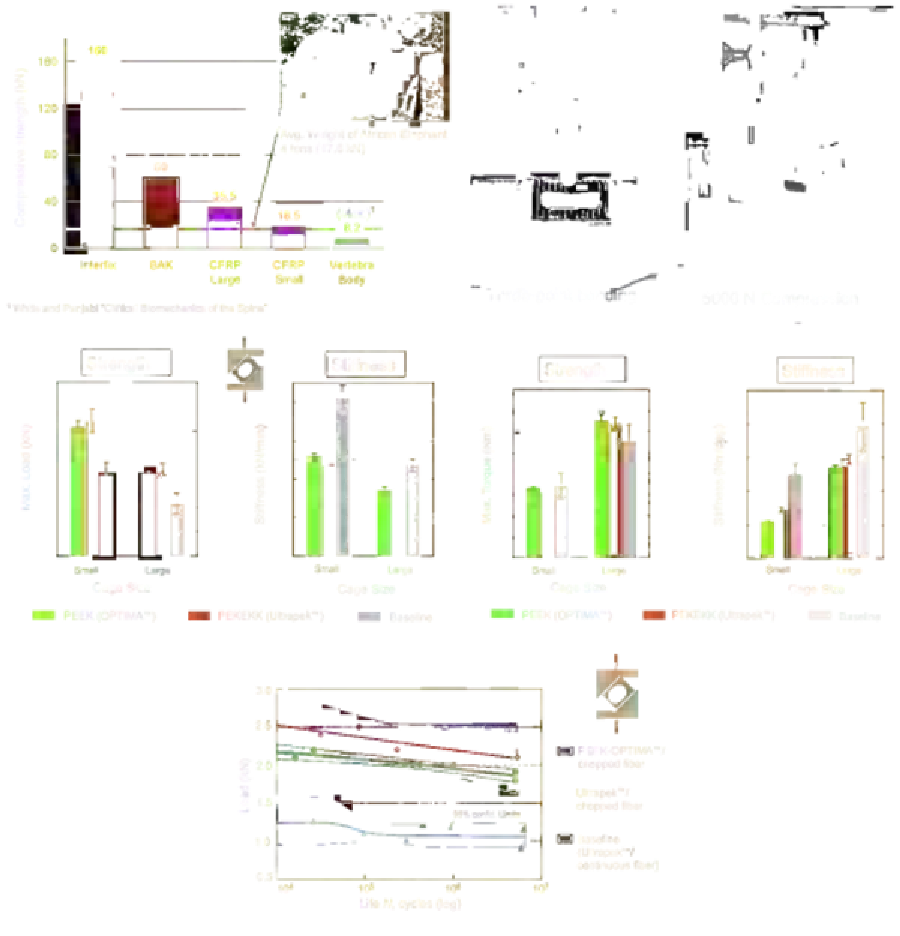
Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
(E)
Figure 13.6
CFR-PEEK and CFR-PEKEKK cages were subjected to an extensive in vitro mechanical testing program,
including static axial compression (A, B), compressive shear (C), torsion (D), and fatigue testing (E). Image courtesy of
Bill Christianson, DePuy Spine.
These excellent fusion results were also reflected
in a 2-year study of reinforced Ultrapek cages in
Spanish goats
[31]
. In this animal study, PAEK
cages were compared with sterilized allografts
(
Fig. 13.7
). Additional goals of the study were to
verify the biocompatibility of the device and
potential wear debris in a functional animal model.
Fusion was observed radiographically after 2-year
follow-ups (
Fig. 13.8
). Histology confirmed exten-
sive growth of trabeculae into the cages (
Fig. 13.9
)
and the absence of an inflammatory reaction
(
Fig. 13.10
).
Based on the encouraging fusion results from the
pilot clinical study and animal study
[30,31]
,
a prospective, multicenter IDE study was initiated for
the FDA in November 1991
[32]
. A total of 221
patients received a carbon-reinforced PEKEKK cage
with posterior pedicle screw fixation. The authors
reported successful fusion in 176 of the 178 (98.9%)
patients who reached 2-year follow-up. Although