Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
of the surfaces on the cells to be evaluated
[21,108,109]
. Initial cell adhesion has been reported
to be a useful tool to gauge cytocompatibility
[110]
.
The representative scanning electron micrographs
shown in
Fig. 10.6
illustrate the HOB cell attachment
to the unmodified PEEK after 1 day in culture in
which very few cells can be seen to have attached.
The surface of the unmodified PEEK does not
promote cellular adhesion and so there are only a few
cells attached, and the cells attached appear to be
lifting off, which may be as a result of the SEM
fixation procedure. In comparison, the modified
surface shows the cells from the day 1 time point to
be more spread and also at the later time points the
cell densities were much greater than that on the
unmodified surfaces, confirming the higher cell
densities, and thereby higher rate of proliferation.
This continues to the 28-day time point, where the
HOB cells on the modified surfaces had formed
layers and there were some mineral deposits
apparent, although HOB cells on the unmodified
surfaces had not managed to form a confluent
monolayer, even at this later time point, and cells are
observed to be poorly attached. The HOB cell
densities on the unmodified and modified PEEK
surfaces were compared with those on the titanium
surfaces. From day 1 postplating, there was a signif-
icant difference in the cell densities on the modified
titanium surfaces compared to unmodified PEEK.
The rate of proliferation was significantly higher on
these surfaces compared with unmodified PEEK
from day 1 onward. The cells reached confluence on
the modified titanium, and Thermanox (THX, Nunc,
DK) between 7 and 14 days, whereas the unmodified
surfaces only reached confluence after 14 days. The
cell densities on the modified PEEK, titanium, and
THX were significantly higher throughout the inde-
pendent 28-day experiments. These findings indicate
that the modified PEEK surfaces with higher C
]
O
and O
e
C
]
O functional group concentrations
promote higher initial HOB cell attachment, and this
trend continues to 21 days. As a result of confluence
being reached earlier on the modified surfaces, the
alkaline phosphatase (ALP) expression, a phenotypic
marker of osteoblast differentitation, was observed to
be more characteristic, leveling off with mineraliza-
tion, although on the unmodified PEEK, the
production of ALP continued to increase for 28 days.
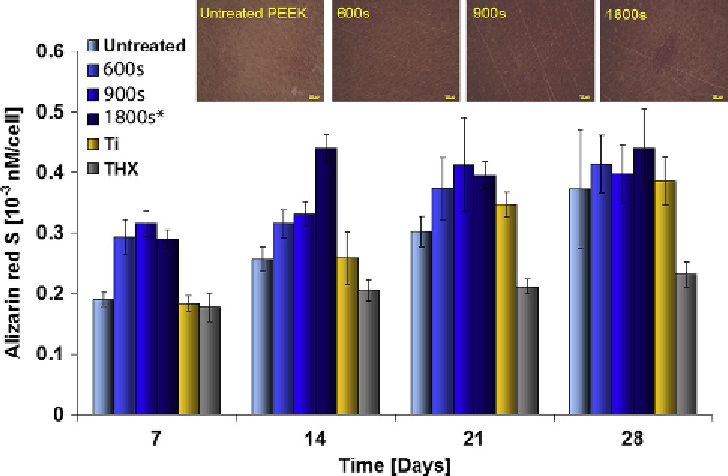
To confirm the mineralization observed at the later
time points by SEM, mineralization was evaluated by
alizarin red S (ARS) staining of calcium deposits by
the cells, shown in
Fig. 10.7
.
Figure 10.7
Mineralization was quantified by dissolving the alizarin red S (ARS) staining of calcium deposition by the
HOB cells. The level of mineralization was higher on all the modified PEEK surfaces from 7 days onward, indicating
that the cells had started to mineralize earlier on these surfaces. The 1800 s modified PEEK surfaces had significantly
higher levels of mineralization throughout the 28-day experiments and showed similar levels to titanium at the later
time points (
SD,
n
¼
3).