Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
on the test method as long as some geometrical
conditions are preserved.
The same type of specimen can be used for
determining the fatigue strength, thus subjecting the
material to cycling loading conditions and counting
the number of cycles to fracture. By repeating the test
at various loading levels, a fatigue curve can be
obtained and plotted on a graph, such as in
Fig. 9.9
.
The load level at which the material sustains the
cycling loading without rupture, or at which failure
occurs at an elevated number of cycles (e.g., 10
7
cycles), is defined as fatigue strength or fatigue limit.
The fatigue curve is affected by parameters such as
wave form, frequency, minimum and maximum
applied load, and specimen geometry, and it is
therefore not only material related but also method
dependent. Care must be taken when comparing
fatigue
material may indicate the presence of impurities or
a chemical modification of the original chemical
structure. In the case of PEEK, the FT-IR technique
can be used to verify the absence of thermal or
photodegradation.
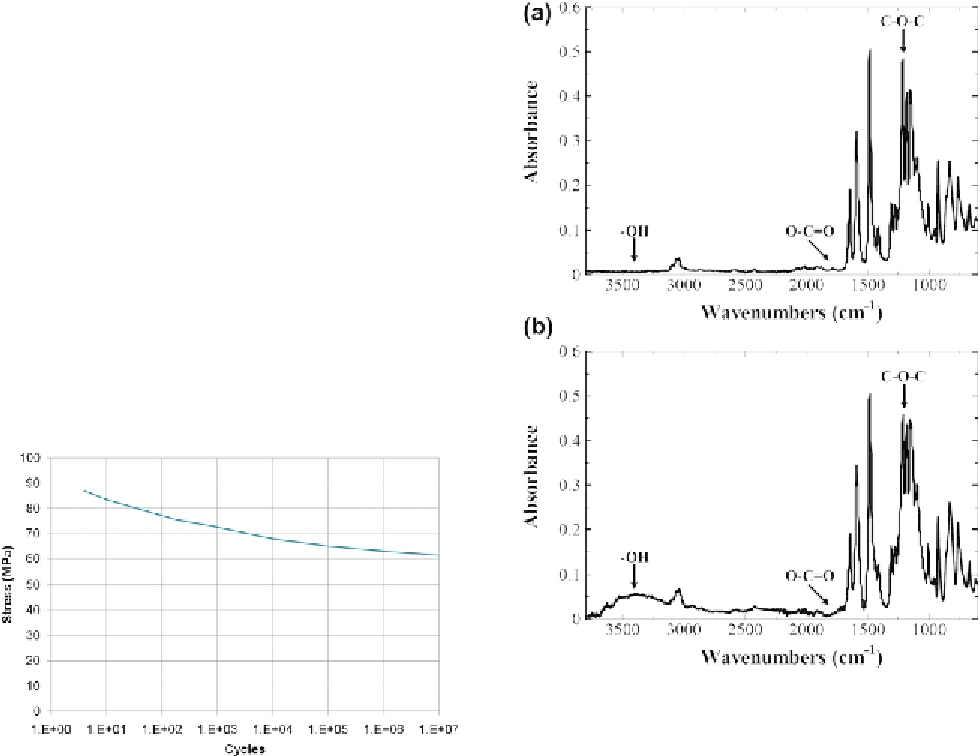
Figure 9.10
shows the differences
in the IR-absorbance spectra of a PEEK sample
before and after exposure to UV irradiation
[78]
.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, also
known as ESCA, an abbreviation for electron spec-
troscopy for chemical analysis) is a chemical analysis
technique that measures the elemental composition,
empirical formula, chemical state, and electronic
state of the elements present on the surface. A typical
XPS spectrum is a plot of the number of electrons
detected (sometimes per unit time) versus the binding
energy of the electrons detected.
values
generated
in
different
testing
conditions.
Mechanical strength and fatigue resistance can be
determined also in a flexural testing configuration, as
described, for example, in ISO 178 or in ASTMD790
[75,76]
. Rectangular samples are used in this case,
and the most commonly used size is 10 mm
4mm
80 mm for ISO and 3.2 mm
12.7 mm
125 mm
(0.125
00
5.0
00
) for ASTM.
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) is
used to obtain an infrared spectrum of absorption of
a solid, liquid, or gas
[77]
. A typical FT-IR spectrum
is a plot of the intensities of the absorbed or trans-
mitted light versus its wavenumber. The infrared
spectrum is characteristic of the molecular repeating
units, and the presence of additional bands in the
infrared spectrum compared with the reference
0.5
00
Figure 9.10
FT-IR spectra of PEEK sample before (a)
and after (b) exposure to UV irradiation. UV photons
react with the aromatic ether bond (decrease of
CeOeC peak around 1215 cm
1
), and form eOH and
OeC]O groups (increase of absorbance in the region
3100e3700 cm
1
Figure 9.9
Tensile fatigue curve for PEEK Optima
LT1
at 23
C. Adapted from PEEK Optima
Data Sheet,
Invibio Ltd.
and around 1730 cm
1
). Adapted
from Ref.
[78]
.