Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
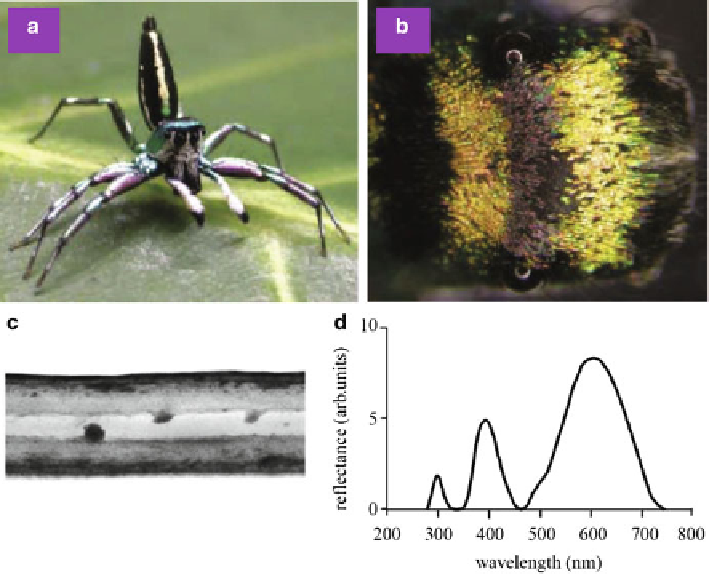
Fig. 8.15
(
a
) Male jumping spider
C. umbratica
.(
b
) Dorsal view of the cephalothorax, showing
two bars of green-orange reflecting scales. (
c
) Cross-sectional TEM image of a colored scale,
showing a sandwich structure. (
d
) Measured reflection spectrum of the colored scales (Reproduced
from [
67
])
The multilayer in
S. willdenowii
consists of two alternating layers with a period
of about 80 nm at the outer cell wall of the adaxial epidermis, producing blue
structural coloration. Similar multilayers exist also in the leaves of the Malaysian
rain forest understory plants
Diplazium tomentosum
,
Lindsaea lucida
,
Begonia
pavonina
,and
Phyllagathis rotundifolia
[
72
],asshowninFig.
8.16
a-c. Iridescent
leaves were also found in the ferns
Danaea nodosa
and
Trichomanes elegans
[
71
],
as well as in the angiosperms
Phyllagathis rotundifolia
and
Begonia pavonina
[
72
].
In
D. nodosa
there exists a multilayer of cellulose microfibrils in the adaxial cell
walls of the adaxial epidermis. In
T. elegans
the blue-green coloration is caused
by a multilayer with a remarkably uniform thickness and arrangement of grana in
specialized chloroplasts adjacent to the adaxial wall of the adaxial epidermis. In both
B. pavonina
and
P. rotundifolia
the blue-green coloration is caused by a multilayer
of parallel lamellae in specialized plastids adjacent to the abaxial wall of the adaxial
epidermis.
Multilayer structures were also found in the fruits of
Elaeocarpus angustifolius
and
Delarbrea michiana
, as shown in Fig.
8.16
d, producing brilliant blue coloration