Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
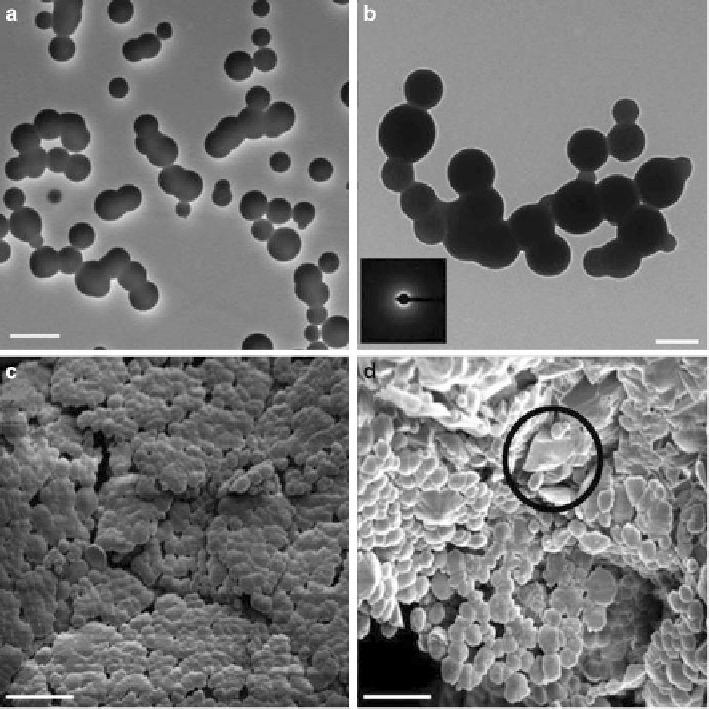
Fig. 6.8
Calcium carbonate particles obtained after 400 s (TEM:
a
,
b
). The low contrast variation
within the particles indicates their liquid character. After complete evaporation, SEM revealed that
spherical solid particles are present along with rhombohedral calcite crystals (
c
,
d
). Scale bars: (
a
)
500 nm, (
b
) 200 nm, (
c
)20
m. On the basis of the morphology of the calcite
particles, the transition to the crystalline phase is assumed to take place through recrystallization.
One rhomboidal calcite crystal is marked by a circle in (
d
). (Reproduced from [
77
], Copyright ©
2008, American Chemical Society)
m, and (
d
)10
growth of CaCO
3
in levitated droplets studied from undersaturated to supersaturated
concentrations in a single experiment (Fig.
6.8
)[
77
]. This amorphous polymorph
formed in the absence of additives at neutral pH. The presence of various species
such as bicarbonate, carbonate, and nondissociated carbonic acid may play an
important role in the stability of ACC. The crystallization procedure of CaCO
3
was
monitored by in situ WAXS experiments performed at a synchrotron microspot
beamline equipped with an ultrasonic levitator. They found that the polymorph
transformation process from ACC to calcite started at the droplet surface and thus