Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
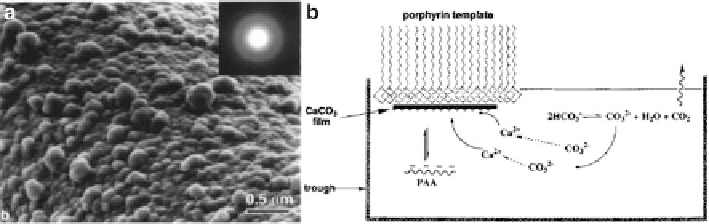
Fig. 6.7
(
a)
High magnification SEM image of the film showing the rough side that faced the
subphase. The inset shows the electron diffraction pattern of the film by TEM. (
b
) A schematic
representation of the experimental setup for preparing CaCO
3
thin films at the interface of the
air/aqueous subphase. (Reproduced from [
64
], Copyright ©1998, American Chemical Society)
Furthermore, Wegner and co-workers investigated that the photochemical de-
composition of pyruvic acid, 4-benzoylphenyl acetic acid and 2-nitro-phenylacetic
gave ill-defined morphologies of calcium carbonate contaminated by organic by-
products [
63
]. Alkaline hydrolysis of dimethyl- and diethyl-carbonate can yield
ACC in form of nanospheres with narrow distribution of radius. The formation of
spherical ACC particles is rationalized in terms of a liquid-liquid phase separation
followed by rapid gelation of the droplet phase of high concentration of CaCO
3
.
A lower critical solution temperature is necessary and its value can be estimated
as 283 K.
6.2.4
The Kitano Method
Xu and co-workers described a strategy in which the slow release of carbon dioxide
by the unstable calcium bicarbonate [
64
]. They have synthesized continuous and
macroscopic calcium carbonate thin films with a thickness ranging from 400 to
600 nm. The thin films were synthesized at air/subphase interfaces by promoting
mineral deposition with amphiphilic porphyrin templates, coupled with growth
inhibition by the use of poly (acrylic acid) as a soluble inhibitor. Films obtained
in the early stage of formation at lower temperature (277 K) revealed characteristics
of a single amorphous phase. The results provide new insights into the biomineral-
inhibitor-template interaction and a new mechanism for synthesizing ACC. The
experimental setup for preparing the amorphous thin film is showed in Fig.
6.7
[
64
]. The Ca (HCO
3
)
2
subphase was prepared by bubbling CO
2
gas into Milli-
Q deionized water in the presence of CaCO
3
for 2 h. Excess solid CaCO
3
was
removed by filtering, and the filtrate was purged with CO
2
for another hour. The
freshly synthesized Ca (HCO
3
)
2
was immediately mixed with sodium polyacrylate
solution to reach a final polymer concentration in the range of 10-40 ppm. Then,
a porphyrin monolayer was deposited onto the surface of the subphase from a