Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
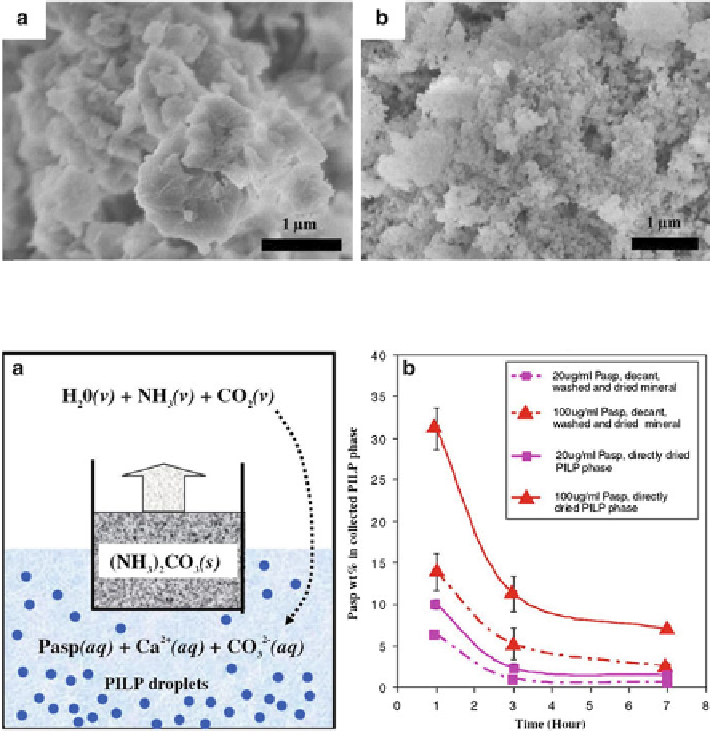
Fig. 6.5
(
a
) FE-SEM image of CCP in as-prepared state and (
b
) that after heating at 373 K for
24 h; the latter in fact corresponds to ACC. (Reproduced from [
56
], Copyright © 2005, Elsevier)
Fig. 6.6
(
a
) Schematic illustration of the experimental setup. A 150-mL glass beaker containing
crushed ammonium carbonate powder was placed in a 500-mL glass beaker containing 250 mL
of a 20 mM CaCl
2
solution with a variable amount of polyaspartate (Pasp). (
b
) Pasp weight
percentage in PILP phase that was collected by centrifugation and dried for elemental analysis,
versus Pasp percentage in PILP phase that was collected by centrifugation, filtered and washed,
and then dried for elemental analysis. Note that the Pasp was distributed both in the mineral and in
the loosely bound water of the PILP phase, and the Pasp percentage of the PILP phase decreased
more significantly during the 1-3 h period. (Reproduced from [
57
], Copyright © 2008, Elsevier)
setupisshowedinFig.
6.6
[
57
]. The (NH
4
)
2
CO
3
in a 150-mL glass beaker was
diffused into 250 mL of 20 Mm CaCl
2
solution containing polyaspartate (Pasp).
When the reaction finished, the solution was centrifuged at 6500 r/min for 300 s and
the precursor product was then collected and dried at 473 K. By using this approach,
the weight fraction of calcium ions and carbonate ions can be estimated, which was
further used to calculate the ratio of carbonate to calcium.