Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
circulation time, nonspecific uptake, and the known ability of dyes to induce
immune response if they are linked to protein-based scaffolds. Linear syn-
thetic poly(amino acids) are also known to have short blood circulations
times, and strong residual negative or positive charge can result in a high
level of kidney uptake and toxicity. However, the immunogenicity of
poly(amino acids) with high degrees of side group modification with various
ligands is usually lower than in the case of proteins. To circumvent
the problems associated with very rapid elimination and immunogenicity
of poly-
L
-lysine, we envisioned using a partial covalent modification of
N-
-amino groups of lysine with activated methoxypoly(ethylene glycol)
(MPEG) esters for increasing the hydrodynamic radius and, consequently,
increasing circulation times of imaging sensors
in vivo
. The resulting graft
copolymer (termed protected graft copolymer, PGC,
Fig. 9.3
) has since
been used successfully for many imaging and drug delivery applications
(reviewed in Ref.
66
) (see
Table 9.1
). One of the benefits of PEGylation
(i.e., covalent linking of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) to other molecules
or surfaces) is that, because of the very high level of water hydration (three
molecules of water coordinate with a single ethylene oxide monomer within
PEG polymer) and very high segmental flexibility, MPEG molecules create
a shell of “soft matter” around the central backbone of polylysine. As a con-
sequence, the backbone and the fluorochromes covalently linked to it are
protected from rapid elimination from the bloodstream. Another important
property of PEG is
e
the ability to protect biomacromolecules
from
A
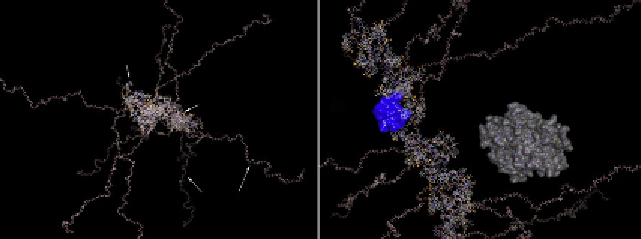
B
MPEG chain
Cyanine
dyes
PLL Backbone
Cyanine
dye pair
Cathepsin B
MPEG protective
chains
Figure 9.3 Molecular operating environment (MOE) modeling the structure of PGC
fragment (n¼20 lysine monomers) with a backbone PLL conjugated to IRDye
800CW cyanine dyes. (A) Main structural elements and (B) the same model showing
the backbone with more detail. The molecular interacting surface of a pair of interacting
IRDye 800CW dyes (H-dimer) is rendered in blue. A molecule of cathepsin B is shown for
comparison.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search