Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
8. PHENOXAZINE DYES
8.1. Overview
The use of a phenoxazine core yields small fluorophores with significant bat-
hochromic shifts in comparison to analogous fluorescein and rhodamine
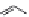
dyes. Examples of this dye class are shown in
Fig. 1.6
. The most widely used
oxazine dye is resorufin
62
, which exhibits
l
max
/
l
¼
572/585 nm,
em
0.74 as the anion.
98
Like fluoresceins,
resorufin is most fluorescent as a phenolate (p
K
a
10
4
M
1
cm
1
, and
e
¼
5.6
F
¼
5.8), making alkylation
or acylation a useful strategy to suppress fluorescence. However, owing
to the structure of the resorufins, only one blocking group can be attached;
the resulting
O
-alkyl or
O
-acylresorufins do not display the complete color
change of the xanthene dyes and still absorb visible light.
99
This complicates
multicolor experiments using resorufin-based fluorogenic compounds.
Another strategy to control fluorescence is through oxidation or reduction
chemistry, with both transformations causing a significant decrease in
fluorescence.
3,100
The amine-containing phenoxazine dyes such as Nile Red (
8
) and
Cresyl Violet (
63
), although less utilized as fluorogenic probes, exhibit useful
¼
+
O
N
O
O
HO
O
H
2
N
O
NH
2
N
N
N
63
62
8
Enzyme substrates
Photoactivatable fluorophores
O
2-
O
3
PO
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
I
N
O
N
N
N
O
N
64
65
66
O
O
O
O
O
O
OH
HO
NO
2
N
O
OH
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
73
HO
O
Indicators
N
N
67
68
O
O
HO
O
OH
HO
O
O
B
O
B
O
O
N
N
H
O
O
74
69
70
NO
2
-
O
3
S
S
S
S
S
H
N
H
N
+
As
As
+
N
O
peptide
H
2
N
O
-
O
3
S
S
HO
O
O
O
O
O
NO
2
N
N
N
71
72
75
Figure 1.6 Phenoxazine-based fluorogenic molecules.





















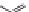


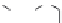

























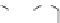































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search