Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
A
IR reporters/phocuses
Insulin receptor
phosphorylation
Donor
FRET
Linker
P
Acceptor
PTB
Substrate
B
Histone phosphorylation reporter
Histone
phosphorylation
Donor
Linker
FRET
P
Acceptor
Histone H3
peptide
1433
C
MLCK reporter
Ca/calmodulin
binding
Donor
FRET
Ca/Cam
Ca/Cam
Acceptor
Donor
Acceptor
MLCK
MLCK
D
CamKII reporter / Camui
CamKII activation
FRET
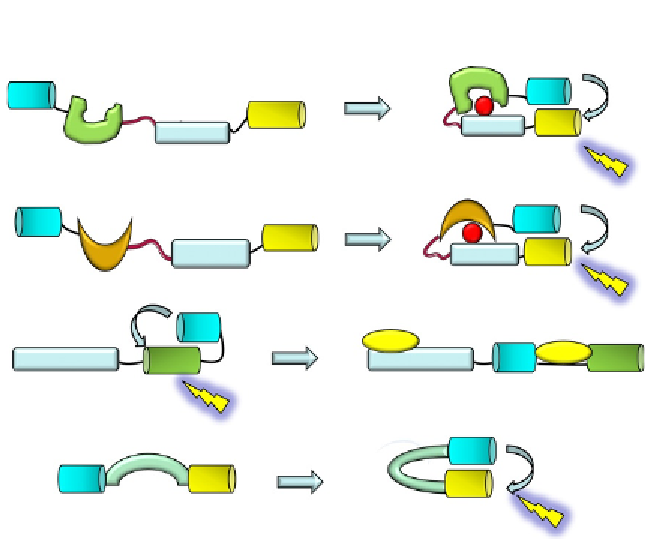
Figure 6.7 Genetically encoded biosensors of other kinases. (A) Phocuses are fluorescent
indicators that report on phosphorylation by the insulin receptor based on CFP/YFP
FRET pair, a substrate peptide for the insulin receptor, a flexible linker sequence, and
a phosphorylation recognition domain.
59
(B) Histone phosphorylation reporter by
appending a substrate sequence from histone H3 bearing a phosphorylatable serine
residue to a phosphoserine-binding domain, derived from 14-3-3, flanked by YFP
and CFP, respectively.
62
(C) MLCK-FIP is a reporter of MLCK activity associated with
Ca
2
þ
/calmodulin binding. This reporter is based on a calmodulin-binding domain de-
rived fromMLCK and a BFP/GFP couple that undergoes FRET in the absence of Ca
2
þ
and
calmodulin.
63
(D) Camui, a FRET biosensor of CaMK II, constituted of full-length CaMKII
flanked by CFP and YFP, allows measurement of CaMKII activation associated with a
conformational change.
55
Upon phosphorylation, the intramolecular interaction between the substrate
and the phosphorecognition domain promotes a conformational change
which induces a consequent increase in FRET between CFP and YFP.
Lin and Ting engineered a histone phosphorylation reporter by
appending a substrate sequence from histone H3 bearing a phosphorylatable
serine residue to a phosphoserine-binding domain derived from 14-3-3
flanked by YFP and CFP, respectively
62
(
Fig. 6.7B
).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search