Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
PKA/PKC signaling. Aurora and Plk kinases are mitotic kinases whose cen-
tral function and subcellular dynamics have recently been uncovered, thanks
to fluorescent reporters of their activity. A biosensor of Aurora B kinase was
developed to study the dynamics of protein phosphorylation by this mitotic
kinase during anaphase.
49
This biosensor encodes a CFP/YFP FRET pair of
AFPs, an Aurora B substrate peptide, and an FHA2 domain and was further
targeted at chromosomes (histone H2B fusion) or centromeres (CENP-B
fusion) (
Fig. 6.6A
). Fluorescence imaging of Aurora B, thanks to this FRET
sensor in mitotic cells, revealed that Aurora kinase activity organizes the
targeted microtubules to generate a structure-based feedback loop and a spa-
tial phosphorylation gradient of multiple substrates during anaphase that pre-
dicts the cellular cleavage site. Along the same lines, a genetically encoded
FRET biosensor of the mitotic Plk1 kinase was developed to probe the
activity of this kinase in human cells in a physiological context and upon
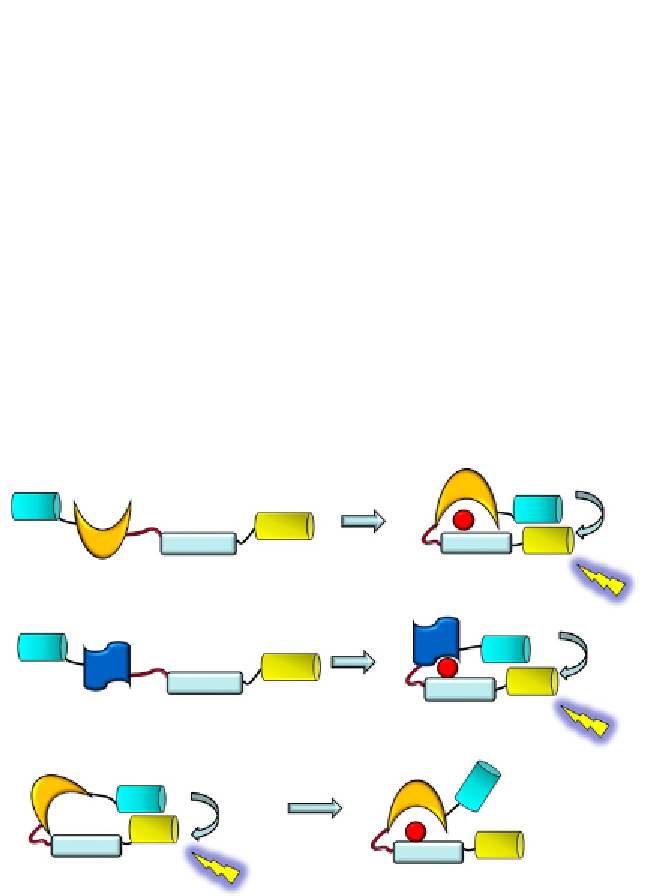
A
Aurora B reporter
Aurora
phosphorylation
Donor
FRET
Linker
P
Acceptor
FHA2
Substrate
B
CDK1/Cyclin B reporter
CDK1/cyclin B
phosphorylation
Donor
FRET
Linker
Acceptor
P
PBD
Substrate
C
ATM reporter
ATM
phosphorylation
FHA2
FRET
P
Substrate
Figure 6.6 Genetically encoded biosensors cell cycle kinases. (A) Aurora B kinase reporter
encodes a CFP/YFP FRET pair, an Aurora B substrate peptide, and an FHA2 domain.
49
(B)
CDK1/cyclin B kinase reporter comprises an autophosphorylation site from cyclin B1
fused to the PBD of Plk1 and flanked bymCerulean and YPet.
56
(C) ATM reporter encodes
a CFP/YFP FRET pair, an FHA phosphobinding domain, and an ATM substrate sequence,
the phosphorylation of which promotes a conformational change of the biosensor
which disrupts FRET between the AFPs.
54
Search WWH ::

Custom Search