Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
N
N
+
+
N
+
N
+
H
2
N
O
NH
2
N
O
N
O
O
CO
2
-
CO
2
-
CO
2
-
CO
2
-
49
50
51
52
Enzyme substrates
Photoactivatable fluorophores
N
N
O
O
peptide
O
peptide
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
NO
2
N
O
N
NO
2
53
O
O
N
O
N
N
O
N
N
O
N
CO
2
H
57
N
N
2
O
O
O
Cl
N
54
O
58
59
O
CO
2
H
CO
2
H
O
O
N
N
Indicators
N
O
O
O
N
+
O
N
O
N
O
N
O
N
NH
2
O
55
HO
2
C
N
CO
2
H
NO
2
O
O
60
N
N
O
HO
2
C
N
CO
2
H
S
O
O
O
59
N
O
N
NO
2
O
O
S
56
61
Figure 1.5 Fluorogenic molecules based on rhodamine derivatives.
modification causes a useful shift in photophysical properties, full alkylation
precludes attachment of blocking groups by acylation. Compound
52
(Q-
rhodamine) balances these two effects, as partial alkylation with a rigid
tetrahydroquinoline moiety yields the desired shift in wavelength (
l
max
/
¼
l
537/556 nm), but
still allows acylation to produce fluorogenic
em
compounds.
67,81
In addition to acylation of the nitrogen substituents, the zwitterionic
nature of the rhodamine structure in aqueous solution allows a mode of
fluorescence modulation that is unique to the rhodamine and isologous dyes.
Amidation of the
ortho
-carboxyl groups on the pendant phenyl rings
prompts
the formation of nonfluorescent
rhodamine lactams, which
can serve as photoactivatable dyes
82,83
and irreversible fluorescent

















































































































































































































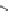

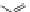
































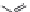






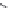



































































































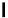







Search WWH ::

Custom Search