Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
HO
O
O
HO
O
OH
HO
O
O
HO
O
O
F
F
Cl
Cl
O
CO
2
H
CO
2
H
CO
2
H
O
2-open
2-closed
35
36
Enzyme substrates
Photoactivatable fluorophores
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
Cl
Cl
O
O
O
O
CO
2
H
NO
2
NO
2
F
F
O
1
37
O
45
OH
HO
CO
2
H
RO
O
OR
38
: R=PO
3
2-
39
: R=SO
3
-
40
: R=
O
OH
HO
Indicators
O
N
O
S
HO
O
O
41
: R=
O
N
O
CO
2
H
CO
2
H
OH
HO
46
NH
2
O
O
O
O
OH
NH
O
O
O
HO
O
O
O
O
Cl
Cl
O
42
OH
43
O
47
HO
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
Cl
Cl
O
O
HO
2
C
N
CO
2
H
O
O
O
O
HO
2
C
N
CO
2
H
44
48
Figure 1.4 Fluorogenic molecules based on fluorescein.
6.2. Enzyme substrates
Fluorescein diacetate (
1
;
Fig. 1.4
) is the archetypal enzyme substrate.
Rotman and Papermaster showed that this lipophilic compound could cross
biological membranes and be hydrolyzed by esterases inside living cells.
57
Diacylfluoresceins are widely used as esterase and lipase substrates and to de-
liver fluorescein-containing molecules to cells.
3,58
Fluoresceins can also be
reduced to form leuco-fluorescein (i.e., fluorescin) derivatives, which are
useful probes for reactive oxygen species (ROS). Compound
37
is a
reduced dichlorofluorescein that is activated by esterases and oxidation.
59
Still other fluorogenic fluorescein diesters can be prepared,
including
diphosphate
38
and disulfate
39
.
60-62
Alkylation of the phenolic oxygens on fluorescein also forces the mol-
ecule into the nonfluorescent lactone form. This strategy has yielded useful













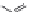




















































































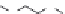


































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search