Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
1
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0
0.7
R
0
R
0
Distance
1.4
R
0
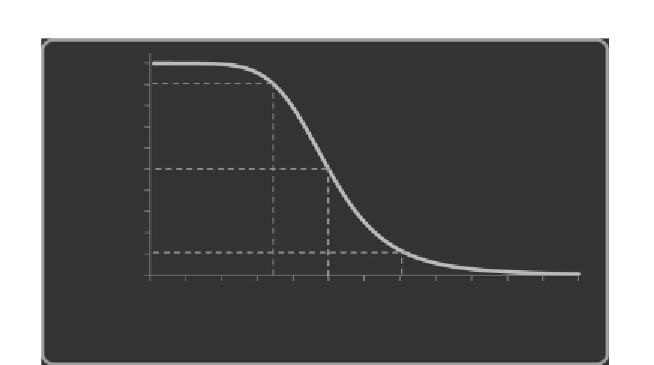
Figure 5.9 FRET efficiency as a function of the distance between the donor and the
acceptor. The FRET efficiency is 50% when the distance is equal to the Förster distance
(
R
0
). FRET efficiencies ranging from 10% to 90% correspond to distances between
fluorophores of 1.4
R
0
and 0.7
R
0
, respectively.
t
DA
t
D
E
¼
1
½
5
:
24
The FRET kinetic measurement can be performed by the calculation of
the ratio (
R
) between the two stationary states' kinetics.
R
is classically used
for measurements by FRET-based biosensors (see next section).
22
Both Eqs.
(5.23) and (5.24)
are applicable only to donor/acceptor pairs
that are separated by a fixed distance. However, single-exponential decays
are rare in biology.
The mean lifetime t
mean
defined by Eq.
(5.15)
has been largely used in
FRET experiments.
8-11
This mean lifetime is then equivalent to the area of
the fluorescence intensity decay, which is related to the FRET efficiency
E
.
However, the mean lifetime does not correspond to the correct average
lifetime, which is defined by Eq.
(5.12)
.
3.6. FRET measurements of molecular populations
In FRET analysis, particularly for biosensors, two elements must be usually
considered: the interacting fluorophore population and the FRET efficiency.
The distance distribution density function
P
(
r
) describes the probability
of finding the specific donor/acceptor pair separation.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search