Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
8.3 WSDL-S
Compared with WSMO, OWL-S, and SWSF, WSDL-S [1] is a rather mini-
malist approach which aims at a direct extension of the existing “traditional”
Web service descriptions in WSDL with semantics (indicated by the last letter
of the acronym). Although the most recent W3C member submissions have
been mentioned in this chapter, the initiative has its roots in the METOR-S
project [110, 132], which has been going on for several years at the LSDIS
Laboratory
2
, Athens, Georgia. WSDL-S was proposed in the form of a mem-
ber submission to the W3C in November 2005 by IBM and the University of
Georgia.
This approach proposes a lightweight mechanism to augment Web service
descriptions in WSDL with semantics. By adding annotation tags to the XML
schema of WSDL, the proposal picks those aspects similar to those in WSMO
capability definitions or OWL-S profiles which appear most relevant to the
authors of WSDL-S.
Using the extensibility of WSDL elements, a set of annotations can be
created to semantically describe the
inputs
,
outputs
and
operations
of a Web
service, as well as to specify a service category in an externally defined ontol-
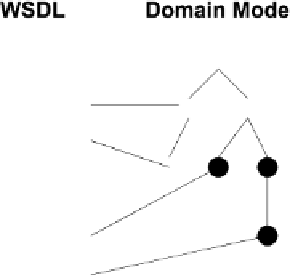
ogy, as is schematically shown in Fig. 8.3.
Fig. 8.3.
Schematic illustration of how WSDL-S provides links to domain models
This method keeps the semantic model outside WSDL, making the ap-
proach impartial in relation to any ontology representation language. The
authors of WSDL-S mention WSML, OWL, and UML as possible candidates.
The advantage of this approach is that it builds upon and stays close to
existing industry standards. The underlying design principles of WSDL-S can
be summarized as follows:
2
See
http://lsdis.cs.uga.edu.

















Search WWH ::

Custom Search