Java Reference
In-Depth Information
Getting started
Before you can apply transformations to shapes, you must be familiar with the steps required
to create simple shapes using JavaFX. See
Drawing simple shapes
from
Chapter 2
,
Creating
JavaFX Applications
for background information on creating simple shapes.
The classes for the Transformation API are kept in the package
javafx.scene.
transform
. You will find several classes there used for different types of transformation,
including
Rotate
,
Scale
,
Shear
, and
Translate
.
How to do it...
To demonstrate the Transformation API, the next code snippet shows the usage of both the
Translate
and the
Scale
transformations on a
Rectangle
shape. You can get the full
code listing from
ch03/source-code/src/transformation/TransformDemo.fx
.
def w = 400;
def h = 200;
def rect:Rectangle = Rectangle {
x: 0 y: 0
width: w - 300
height: h - 150;
fill: Color.BLUE;
stroke: Color.WHITE;
strokeWidth: 3
onMouseClicked:function(e:MouseEvent){
rect.transforms = [
Translate
{x: e.x y:e.y}
Rotate
{angle:45}
];
}
}
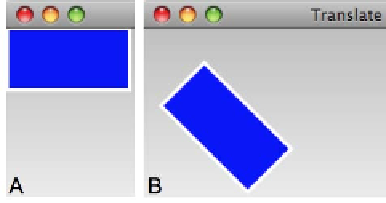
When the code runs and the Rectangle instance (Figure A) receives a mouse-click event, it
applies both
Translate
and
Rotate
transformation operations as shown in Figure B.