Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 2.2.
Marine depositional
environments. Modified from
Kennett (1982).
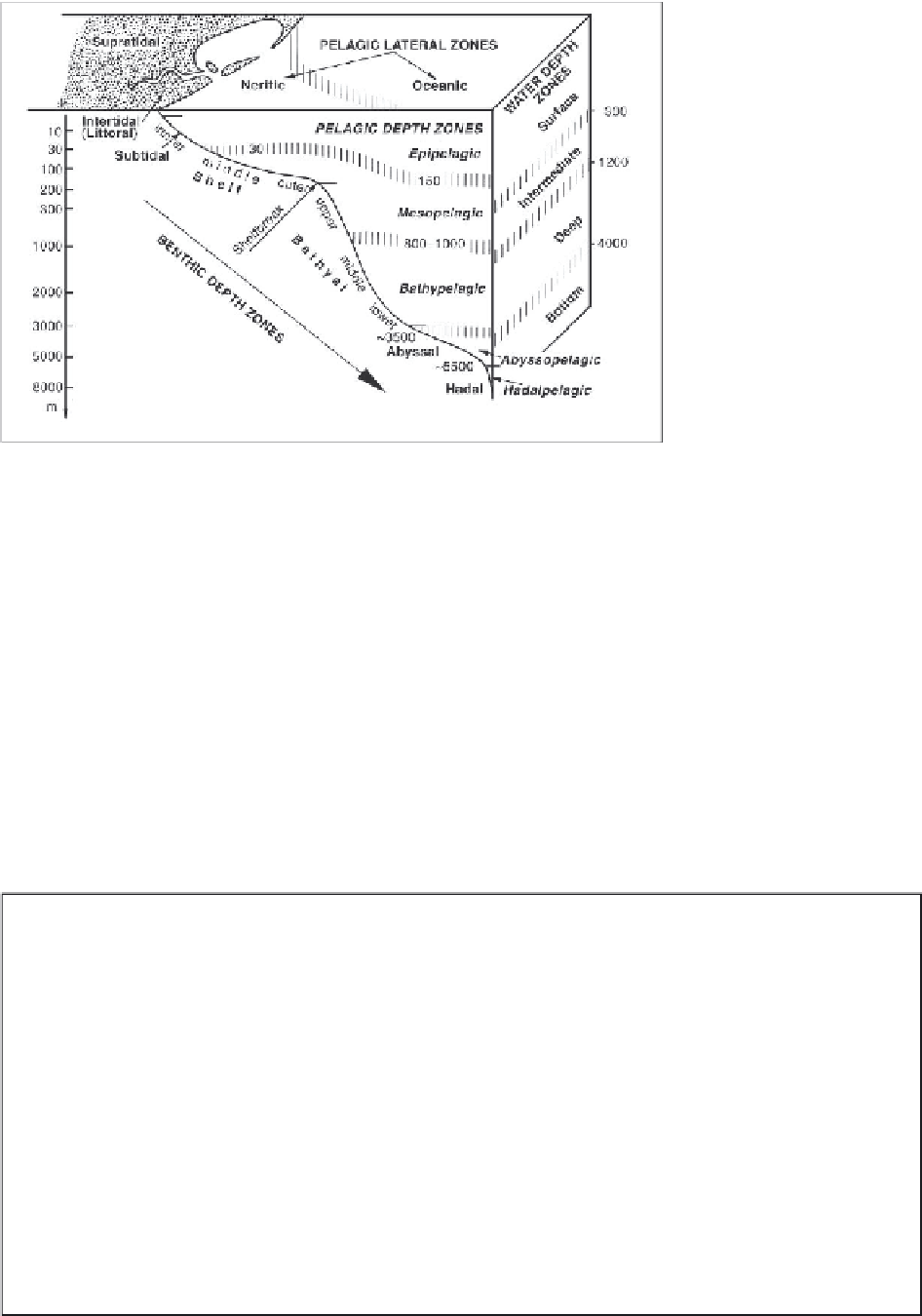
2.3.2 Vertical and Horizontal Zonations
continental shelf), (4) bathyal (approximately equal to
the continental slope), (5) abyssal (corresponding to
the abyssal plains), and (6) the hadal zone (deep-sea
trenches). Modern carbonate sedimentation takes place
within the range of zone 1 to parts of zone 5.
Subdivisions of marine environments are both vertical
and horizontal:
2.3.2.1 Vertical Zonations
-> Geologists are in favor of the terms
supratidal,
intertidal
and
subtidal
instead of the ecologically de-
fined terms supralittoral, littoral and sublittoral.
Benthic depth zones:
The depth of the sea bottom and
critical levels controlling the sedimentation subdivide
the benthic environments into six zones: (1) coastal sub-
littoral zone (above high tide, corresponding to the su-
pratidal zone), (2) littoral (between high and low tide,
identical with the intertidal zone), (3) sublittoral (be-
low low tide, corresponding to the major part of the
Pelagic depth zones:
Five zones are defined by the ver-
tical distribution of floating and swimming life. These
are, in descending order, the epipelagic zone (the up-
per region of the oceans, extending to a depth of about
200 m), the mesopelagic, bathypelagic, abyssopelagic
Box 2.1.
Glossary of terms used in the subdivision of marine environments.
Fairweather wave base (FWWB)
: Intersection of the wave base with submarine topography. The water depth below
which surface wave action no longer stirs and moves the sediment. The depth of the wave base varies widely,
depending on wave amplitude and fetch, bottom topography, activity of storms, orientation of shelves and ramps,
latitudes etc.
High tide:
High water. The maximum height reached by each rising tide.
Low tide
: Low water. The minimum height reached by each falling tide.
Mean sea level
: The average height of the surface of the sea for all stages of the tide for a defined period.
Storm wave base
: See storm wave weather base.
Storm wave weather base (SWWB)
: The water depth down to which storm-generated waves and resulting bottom
currents rework bottom sediments and produce specific texture types (tempestites). The depth of the storm wave base
varies strongly and depends on shelf and shelf edge topography, storm intensity and climate zone.
Surf
: a) The wave activity in the area between the shoreline and the outermost limit of breakers. b) A collective term for
breakers.
Tidal range
: The difference in height between consecutive high and low waters.
Tide
: The periodic rise and fall of the sea resulting from the gravitational attraction of the moon and the sun acting upon
the rotating earth and causing flood and ebb currents.
Wave base
: See fair-weather wave base.