Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
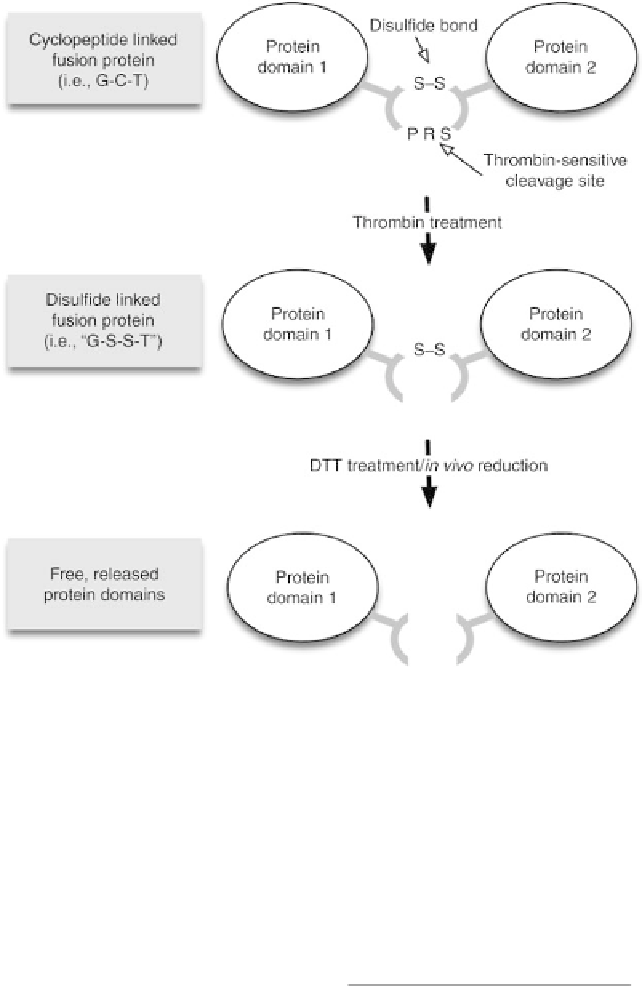
FIGURE 4.1
Design of the dithiocyclopeptide linker. The linker is based on the structure of
somatostatin modified to contain a thrombin-specific sequence, PRS. Two cysteinyl-residues on
somatostatin naturally form a disulfide bond. In vitro thrombin treatment cleaves the thrombin-
sensitive sequence while the reversible disulfide bond remains between protein domains. In vitro
DTT treatment or in vivo reduction is able to reduce the disulfide bond, and release free protein
domains from the fusion protein. Source: Adapted from Reference [45].
of in vitro G-CSF bioactivity, with an EC
50
of 10.12 ng/mL,
compared with the noncleaved, nonreduced fusion protein
(EC
50
¼
TABLE 4.2
In Vitro
Biological Activity of G-CSF-Cyclo-Tf
Fusion Protein with a Cleavable Linker (G-C-T)
23.69 ng/mL). The maximal response of the cleaved
and reduced fusion protein was also much higher than the
intact fusion protein (Table 4.2). As previously mentioned,
the covalent linkage between two functional domains may
cause strong steric hindrance, or block the receptor-binding
site of the protein moieties. These reasons may account for
the decreased bioactivity of many fusion proteins [13,26].
Therefore, the improved G-CSF bioactivity was probably
due to the reduced steric hindrance and decreased blockage
effect with the release of free G-CSF from Tf. This result
indicated that, owing to the in vivo cleavability of the linker,
a fusion protein with this disulfide linker might have better in
vivo biological activity than a comparable fusion protein
with a noncleavable linker.
The in vivo cleavability of the thrombin pretreated,
disulfide-linked fusion protein (designated as G-S-S-T)
was also investigated in animals. G-S-S-T (with cleavable
EC
50
(ng/mL)
a
E
max
(A
570
)
b
Fusion Protein
G-C-T
23.69
0.8
Thrombin and DTT treated G-C-T
10.12
1.9
a
EC
50
, half-maximal effective concentration, as determined by the NSF-60
proliferation assay. The NFS-60 cells proliferate in response to G-CSF
treatment.
b
E
max
, maximal effect, as determined by the MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazole-
2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assay for NSF-60 cell proliferation.
The MTT assay is a colorimetric assay based on the reduction of MTT to
purple formazan in the mitochondria of living cells.
Source: Adapted from Reference [45].
disulfide linker) or G-C-T (with stable dithiocyclopeptide
linker) was administered intravenously to CF1 mice, and the
plasma samples were analyzed by nonreducing SDS-PAGE
followed by anti-G-CSF Western blot analysis. As shown in




Search WWH ::

Custom Search