Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
FIGURE 39.1
Ribbon presentation of the constant domains of an IgG1. Non-CDR loops are
indicated in light gray and the beta sandwich core in dark gray. The structures are aligned such that
the N-terminal ends are on the top and the C-terminal ends are on the bottom.
One attractive extension of the Fcab scaffold concept is the
possibility of creating bispecific or multivalent antibodies.
Modular replacement of the wild-type CH3 domain of an
existing conventional antibody with a CH3 domain binding
another or the same antigen is expected to yield antibody
molecules, which structurally are minimally altered com-
pared to the acceptor antibody. However, such proteins (which
are referred to as mAb
2
) are able to recognize antigen via their
variable domains in a conventional fashion and via the
engineered antigen-binding site located in the CH3 domain
of the Fc. In analogy to the Fcab scaffold, mAb
2
proteins are
expected to retain all functionalities of a normal antibody.
The following sections of this chapter describe the design
and characterization of such bispecific mAb
2
proteins. The
results of these experiments laid the foundation for the
successful proof-of-concept of the mAb
2
approach.
39.3 DESIGN OF LIBRARIES BASED
ON THE HUMAN IgG1 CH3 DOMAIN
For designing the Fcab libraries with mutations in the C-
terminal loops of the CH3 domains, a number of criteria were
applied in order to choose those residues in the sequence that
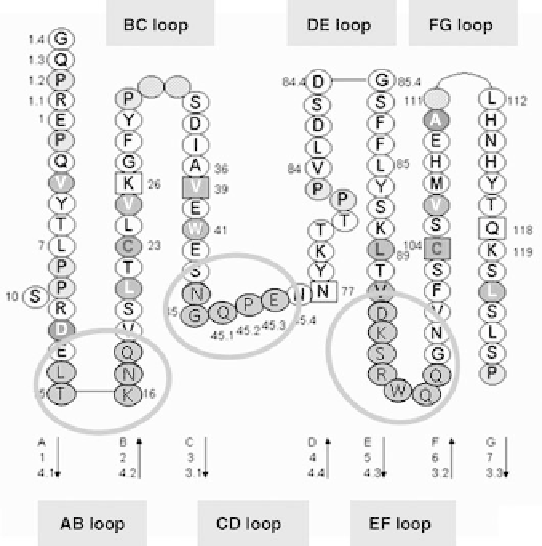
FIGURE 39.2
The fold of the CH3 domain of human IgG1 presented as string of pearls chain form.
Residues that were randomized in the CH3 libraries are encircled and indicated in gray.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search