Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
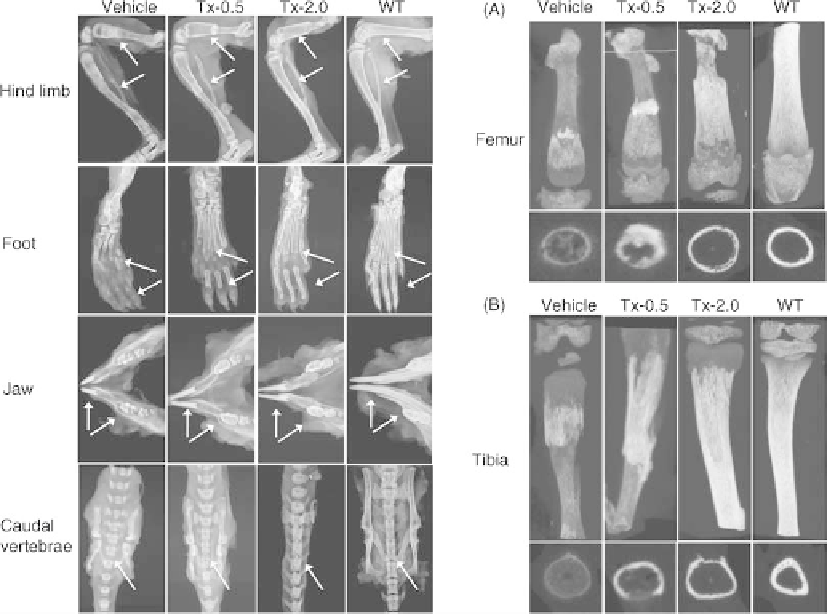
FIGURE 28.3
Left panels: Representative radiographs of hind limb, foot, jaw bones, and caudal
vertebrae specimens from 22-day-old Akp2
/
mice treated with vehicle, 0.5mg/kg/day ENB-0040
(Tx-0.5), or 2.0mg/kg/day ENB-0040 (Tx-2.0), and untreated WT mice (radiographic
magnification 5
). Arrows indicate improved mineralization of tibia, femur, metatarsals, finger
bones, incisors and molars, fracture healing in the tibia and femur, and reduced spaces between
adjacent spinal vertebrae in treated versus untreated mice. Right panels:
m
CT images of (A) femora
and (B) tibiae of 22-day-old Akp2
/
mice treated with vehicle, Tx-0.5, or Tx-2.0 compared with
untreated WT mice. Images clearly show improved tissue mineral density and callus formation at
fracture sites of drug-treated mice. Transaxial views are shown at the bottom. Source: Reproduced
from Reference 28, Bone 49(2): 250-256, August 2011, with permission of the International Bone
and Mineral Society.
disease with death at 14 months of age [47]. Bone marrow
cell transplantation has been attempted in two severely
affected infants with some clinical improvement, but signif-
icant morbidity remains [20,21].
Anabolic treatment with parathyroid hormone 1-34, ter-
iparatide apparently benefitted one adult patient [48]; how-
ever, others have reported even an increase in osteomalacia
with this treatment [49]. Furthermore, prolonged use of this
agent is not recommended nor approved for the treatment of
rickets in children because its use is associated with increased
incidence of osteosarcoma in rats [50]. Some patents have
been filed relevant to an anti-sclerostin agent developed
primarily to treat osteoporosis as a means of promoting
osteoblastic activity and consequently stimulating TNAP
activity inHPP patients [51].My laboratory is also developing
small molecule modulators of TNAP activity that could be
used to upregulate residual TNAP activity seen in some HPP
patients [52]. However, all of these anabolic treatments,
including teriparatide, anti-sclerostin, and TNAP activators,
rely on the existence of a sufficiently mild ALPL mutation
such that the enzyme retains sufficient catalytic activity
amenable to upregulation. Such a circumstance may apply
to a subset of HPP patients, presumably those with milder,
adult forms of the disease or odonto HPP, but will likely not be
effective in more severe forms of the disease.
As described earlier in this chapter, ERT with either
alkaline phosphatase-rich sera from patients with Paget's
disease or purified liver or placental ALP was not found to be
clinically beneficial [16-19]. This outcome could be due to
the short half-life of the administered protein in patients or
lack of homing of the administered enzyme to the site of
mineralization, namely, the immediate environment of chon-
drocyte- and osteoblast-derived matrix vesicles where
TNAP functions
to control PP
i
levels and promote
Search WWH ::

Custom Search