Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
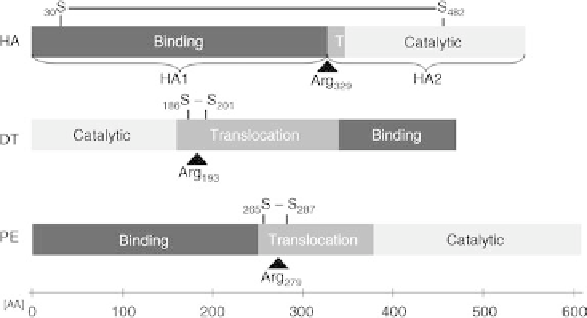
FIGURE 25.4
natural translocation domains for endosomal escape. Many toxins contain trans-
location domains to facilitate endosomal escape to execute their toxic activity in the cytosol. All of
the three domain toxins are cleaved to separate the binding from the catalytic domain. After cleavage,
both are connected by only a disulfide bridge that is usually reduced to separate the subunits. The
hemagglutinin (HA) of the influenza virus contains a very short translocation domain. Diphtheria
toxin (DT) and Pseudomonas exotoxin a (PE) have translocation domains beyond 100 amino acids
[AA]. The triangle shows the position of the proteolytic split.
network involving the KDEL receptor that binds the REDL
sequence of the toxin. The domain II mediates the trans-
location from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cytosol via
low pH induced tryptophane membrane anchor. In the
cytosol, the catalytic domain III rapidly inactivates elonga-
tion factor 2 (EF2) by ADP ribosylation [69].
The immunogenicity risk of the PE translocation
domain II can be reduced by minimizing it to only 10 amino
acids (residues 273-282) while still maintaining its func-
tionality. This was demonstrated with a trimodular fusion
protein containing a single-chain antibody against human
epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2), the minimal
translocation domain of PE, and the BH3-interacting domain
death agonist (BID) to trigger apoptosis. This molecule
efficiently eliminated cancer HER2 positive cancer cells
in an animal model [70]. Truncated translocation domains of
PE have been used frequently to transfer apoptosis inducing
molecules into cells [71].
The diphtheria toxin (DT) is split into two fragments that
are still connected through a disulfide bridge. The amino
terminal fragment contains the catalytic domain, and the
carboxy-terminal polypeptide consists of the translocation
and receptor-binding domain. Attachment to the heparin
binding epidermal growth factor-like precursor (hb-EGF) on
the cell surface triggers internalization via clathrin coated
vesicles, which are then converted into early endosomes.
Upon acidification of the endosomal lumen, the trans-
membrane domain unfolds and inserts a pore into the endo-
some membrane. The reduction of the disulfide bridges
between the two toxin fragments releases the catalytic
domain into the cytosol [72]. Despite its efficient escape
from the endosome, the translocation domain of DT has so
far not been used separately as building block for novel
fusion proteins addressing intracellular targets. Until now,
all therapeutic applications of DT focus on its use as
immunotoxin, utilizing the catalytic domain for ADP ribo-
sylation. Further references can be seen in Part IIb.
Other mechanisms to escape from the endosome can be
derived from viruses. They contain fusogenic peptides that
undergo a conformational change during the lowering of the
pH in the endosomes. For instance, the first 23 N-terminal
amino acids of the hemagglutinin subunit 2 (HA2) of the
influenza virus form a
a
-helix that can insert into the
endosome membrane under acidic conditions. A fusion
consisting of this HA2 derived peptide, p53, and polyargi-
nine as CPP induced apoptosis fivefold more efficient than
the fusion protein without HA2 [73].
On the basis of the observation of pH induced conforma-
tional conversion, an artificial amphiphilic peptide was
designed. Owing to its repetitive nature of the four amino
acids Glu-Ala-Leu-Ala, it was termed GALA peptide. It
consists of 30 residues and changes from a random coil to
a
-helix when the pH is lowered from 7 to 5. The helix inserts
into the endosomal membrane and creates a pore through
which molecules can passage to reach the cytosol [74]. So
far, this peptide has only been used as additive but not as
component of a fusion protein. In Table 25.1 sequences of
translocation domains are collected.
25.4 ORAL DELIVERY
The majority of small molecule drugs can easily traverse
membranes or barriers; hence they are orally administered.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search