Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
between the C-terminus of heavy chain of the antibody
fragment and the N-terminus of the SAg to allow for
structural flexibility. The two Fab chains are held together
by noncovalent forces (Figure 24.1), as the disulfide bond
between the Fab heavy and light chain has been removed.
The protein contains 672 amino acid residues, consisting
of two protein chains of 458 and 214 amino acids.
During production, the expression of naptumomab esta-
fenatox is under the control of the lacUV5 promoter, which
is induced by the addition of isopropyl-
b
-
D
-thiogalactoside
(IPTG) to the culture broth. As the product is found in the
growth medium, standard technology such as centrifugation,
filtration, or expanded bed adsorption is used to remove the
cells. The purification of naptumomab estafenatox consists
of four chromatographic steps. (1) The capture step, per-
formed on a SP Sepharose FF matrix, concentrates the
protein and reduces the levels of process related impurities.
(2) Main purification is performed by affinity chromatogra-
phy on a protein G Sepharose, which utilizes the specific
interaction between protein G and the Fab part of naptu-
momab estafenatox. This removes virtually all non-Fab-
containing proteins, as well as further reducing the levels of
DNA and endotoxins. (3) The polishing step, by ion-
exchange chromatography, is performed on a Source 15S
matrix, which separates some of the isomers of the fusion
protein and reduces impurities. (4) The final step is a gel
permeation chromatography using a Sephadex G-25 Fine
matrix. At this step, a buffer exchange to the formulation
buffer is performed.
The process has been scaled up to 1000 L by Richter-
Helm BioLogics GmbH & Co KG (former Strathmann
Biotec AG), Germany, and material was manufactured for
clinical studies. After process optimization, a total of nearly
40 g has been achieved from the 1000-L process.
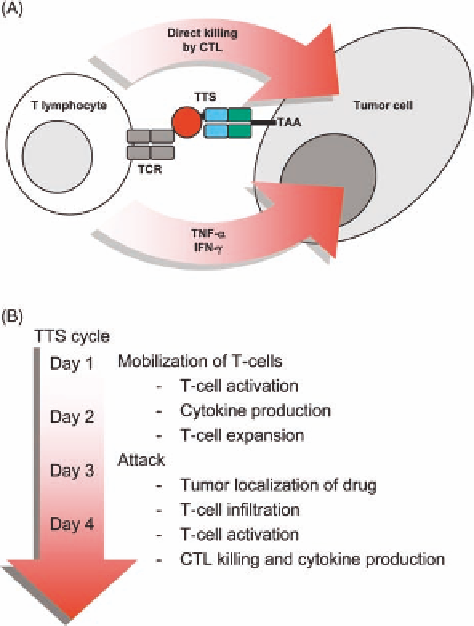
FIGURE 24.2
(A) Mechanism of action for tumor-targeted
superantigens. CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; IFN, interferon;
TAA, tumor-associated antigen; TCR, T-cell receptor; TNF, tumor
necrosis factor; TTS, tumor-targeted superantigen. (B) Schematic
representation of immune/drug functions during a TTS cycle.
be obtained in the growth medium [17]. A useful feature of
these fusion proteins is that they bind protein G and can
therefore be purified using standard affinity chromatography.
As an example, the production of naptumomab estafena-
tox [18] is outlined here. The murine antibody 5T4 is
directed against a tumor antigen found in many carcinomas
(see 24.3). When fusing the mAb 5T4 with the SAg and
expressing the fusion protein in E. coli, it was found that the
5T4 light chain was limiting high expression levels. There-
fore, the 5T4 Fab moiety was engineered to improve
production [17]. The resulting Fv with seven substitutions
in the variable light chain and four substitutions in the
variable heavy chain was designated variant 18 (V18) of
5T4Fv. This variant displays higher affinity for the 5T4
antigen than the wild-type Fab. The 5T4 Fv genes were
fused to the sequences coding for the constant regions of the
murine IgG1/
k
antibody C242 in the expression vector. The
5T4FabV18 coding regions were fused to the coding regions
for a SAg variant extensively engineered to be optimal for
therapy in humans (see 24.4), the SEA/E-120 [19].
The two moieties in the 5T4FabV18-SEA/E-120 mole-
cule (naptumomab estafenatox) also contain a tripeptide
24.3 TUMOR-TARGETED SUPERANTIGENS
ARE POWERFUL TARGETED IMMUNE
ACTIVATORS AND USEFUL FOR ALL
TYPES OF MALIGNANCIES
The TTS prototype fusion molecule (C215Fab-SEA) was
built to target the human tumor-associated antigen
EpCAM/GA733-2/CD326 [20] recognized by the C215
mAb. In this case, the Fab of the C215 mAb was used to
target the SAg-induced T-cell activity against tumor cells
by genetically fusing it with the SAg SEA. A series of
novel TTS molecules have been developed from the pro-
totype (see 24.4), and as a consequence of the engineering
process to optimize the SAg part of the TTS fusion proteins
for human use, many of the new compounds do not activate
murine T cells and are therefore not therapeutically active
in nonhumanized experimental mouse models. Thus,
we have used the C215Fab-SEA fusion protein, which
Search WWH ::

Custom Search