Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
(A)
Untreated
2.5 ug Fc/GITRL
5 ug B7.1/Fc
2.5 ug Fc/GITRL + 5 ug
B7.1/Fc
5
7
9
12
Days
14
16
18
21
1
(B)
Untreated
2.5 ug Fc/GITRL
30 ug Fc/CD137L
2.5 ug Fc/GITRL + 30 ug
Fc/CD137 L
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
5
7
9
12
Days
14
16
18
21
FIGURE 19.8
(A) Fc-GITRL
þ
B7.1-Fc and (B) Fc-GITRL
þ
Fc-CD137L combination therapy in
COLON 26-bearing BALB/c mice showing enhanced tumor regression compared to treatment with
either reagent alone.
immunotherapy for the treatment of cancer, it is important to
have a comprehensive understanding of how the immune
system is regulated. There is now abundant evidence from a
number of diverse experimental systems that a sub-
population of CD4
T
reg
cells [101]. Although CD4
cells were first
discovered in mice [102], a population with similar pheno-
typic and functional properties has been defined in humans
[103-107]. Since clinical trials to reduce or delete T
reg
cells
in the setting of cancer immunotherapy have not been
performed, the potential of this procedure in humans is
currently unknown. Evidence however, is accumulating
that T
reg
cells are more abundant in the peripheral blood
and tumor microenvironment of cancer patients and may be
responsible for
þ
CD25
þ
T cells, collectively termed T
reg
cells,
is present in normal mice and is essential for both homeosta-
sis and the maintenance of tolerance to tissue-specific anti-
gens [92-95]. It is now generally agreed that these cells
display the CD4
þ
phenotype and the FOX3p geno-
type [96] and that they exert their activity either by cell-cell
contact [21] or by secretion of inhibitory IL-10 or TGF-
b
cytokines [97,98]. Another discovery with the immuno-
suppressive effects of CD4
þ
CD25
þ
the observed tolerance displayed in
patients [108].
T
reg
cells is that immu-
nocompetent mice bearing syngeneic tumors become
tolerant to their tumors by day 9 after transplantation
when CD4
þ
CD25
þ
19.5.1 LEC Fusion Proteins in Combination with T
reg
Depletion
To evaluate the subpopulation(s) of T cells responsible for
the observed tumor destruction, depletion studies were
performed in conjunction with the above therapy studies
[15]. One day after COLON 26 tumor implantation, mice
received cytotoxic antisera specific for CD4
appeared in the peripheral circulation
[99,100]. Depleting T
reg
cells before or at the time of
implantation with a rat mAb PC61 will produce either
incomplete tumor reduction or a delay in tumor growth.
Moreover, tumor suppression could also be produced by
low dose whole-body irradiation or cyclophosphamide
chemotherapy, which has been found to be cytotoxic to
þ
CD25
þ
,or
NK cells. Each of these antisera was administered every
5 days, reducing the appropriate cell subpopulation to
þ
, CD8
þ
2%
<



















































































































































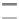










Search WWH ::

Custom Search