Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
be considered. IgG1, IgG2, and IgG4 all have a circulating
half-life of 21 days while IgG3 only has about a week. Other
factors for consideration include significant structural dif-
ferences at the hinge regions between different isotypes, and
structural differences in the oligomeric state of IgG, for
example, the dimeric structure of IgA and the pentameric
structure of IgM, which result in different valencies. The
number of allotypic variants of the isotype is also an
important factor, since a molecule of one allotype can be
potentially immunogenic for individual patients having a
different allotype [77,79].
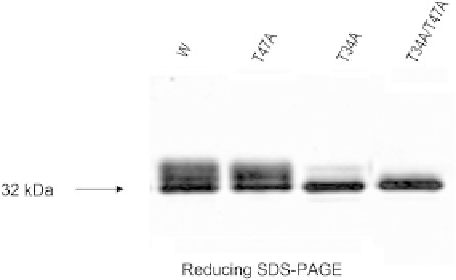
FIGURE 8.5
Western blot analysis. Cell supernatants probed
with an anti-peptide region antibody showed that the O-linked
glycosylated protein and mutants with removed individual or both
O-linked glycosylation sites.
8.6.7 Tailoring Fc-Effector Functions
to Fit Individual Needs
Even though the different Fc isotypes have different degrees
of Fc-effector functions, further protein engineering efforts
to enhance or silence the Fc functions are sometimes
required to optimize the particular mode of action of indi-
vidual drugs.
Efforts to improve Fc-effector functions were fueled by
clinical trials of Rituxan, in which patients who expressed a
higher binding allotype of Fc
g
RIIIa showed significantly
better clinical responses to Rituxan than patients who
expressed the lower binding allotype of the receptor [99].
Much effort was focused on engineering the receptor-bind-
ing site on the Fc to enhance the Fc
g
RIIIa-binding affinity
and as a result, activity was enhanced as much as 100-fold in
in vitro ADCC assays [100]. XmAb2531, an Fc-engineered
anti-CD30 antibody with enhanced ADCC activity from
Xencor Inc. (Monrovia, CA), is in Phase 1 clinical trials
for the treatment of patients with lymphomas. On the other
hand, since Shields et al. demonstrated that antibodies
expressed from a fucosylation-deficient Chinese hamster
ovary cell line, Lec13 cells, had up to a 50-fold increase
of binding activity of Fc
g
RIIIa and a significant increase of
ADCC activity [101], efforts lately have been focused on
developing production cell lines that produce either low
fucosylated or nonfucosylated IgG. A recent structural study
demonstrated that Fc with or without core fucose on its CH2
domain have significantly different conformations [102]. A
number of antibodies containing no, or significantly
reduced, core fucose are currently in clinical trials [103].
For Fc-fusion proteins targeting cell surface receptors,
including receptor agonist peptide-Fc therapeutics, there is a
need for an Fc domain that does not possess any effector
function to destroy cells, yet retains the pharmacokinetics
and other favorable properties of IgG. Early efforts to
eliminate Fc-effector functions were focused on mutations
of the Fc
g
R-binding sites in the lower hinge region of the Fc
to reduce Fc
g
R-binding activity [96]. Both IgG1 and IgG4
mutants, in which residues at positions 234 and 235 were
changed to Ala, showed at least 100-fold reduction of
Fc
g
RI- and Fc
g
RII-binding activities [104]. For example,
amount of protein missing these three amino acids was not
correlated to the protein expression level, harvest time, or
cell viability. After ruling out other possibilities, we hypoth-
esized that these three amino acids were removed by a signal
peptidase due to a secondary recognition site. The problem
was solved by changing to a different signal peptide
sequence in this expression construct (data not shown).
8.6.6 Isotype Selection
Fc-dependent activities that recruit or activate components
of the innate or adaptive immune system are sometimes very
important for the efficacy of antibodies and Fc-fusion pro-
teins. Fc-effector functions include (1) CDC, triggered by
the complement cascade at the cell surface, (2) ADCC, and
(3) antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP). For
the IgG antibodies, both ADCC and ADCP are initiated by
the engagement of the lower hinge region of the Fc with Fc
g
receptors (Fc
g
Rs) on the surface of immune effector cells,
leading to the lysis of the targeted cells or phagocytosis.
There are four different isotype classes of human IgG,
and each isotype has different levels of effector functions
associated with it. IgG4 does not activate the complement
cascade and binds weakly to Fc
g
Rs except Fc
g
RI [76,77],
whereas IgG2 does not bind to Fc
g
Rs on mononuclear cells
or neutrophils, except the allotypic variants of Fc
g
RIIa
[77,78]. Depending on the mechanism(s) of drug action,
different isotypes can be selected based on the desired
strength of Fc-effector functions. For example, IgG1 is
the most common choice for antitumor drugs, which require
strong ADCC and CDC activities. In contrast, IgG2 and
IgG4 are better choices for agonist drugs, since stimulating
certain cellular functions, not killing the target cells, is their
main goal. The fact that IgG1can be efficiently purified on a
protein-A column also contributes to its popularity. The
difference of serum half-life is another important factor to
Search WWH ::

Custom Search