Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
A
B
Scanner
system
Scanner
system
Laser
Laser
Movable
table
Powder
bed
Roller
Object
being
fabricated
Vat
Photopolymer
Powder-
delivery
system
Fabrication
piston
Selective laser sintering
Stereolithography
C
D
Liquid
adhesive
supply
Ink-jet
head
Particle
collector
y
stage
x
−
Powder
bed
Roller
Milling
head
Object and
support
materials
Powder-
delivery
system
Fabrication
piston
3-D printing
Wax printing
Sterile environment
(laminar flow)
Ultraviolet
lamp for
disinfection
E
F
Sterile compressed air
x
z
stage
−
y
−
Sterile
filter
Plotting
medium
Thermostat
Extrusion
nozzle
Plotting material
(with cells)
Plastic filament
supply coil
Ta b l e
3-D objects
(with cells)
Fused deposition modeling
Bioplotter
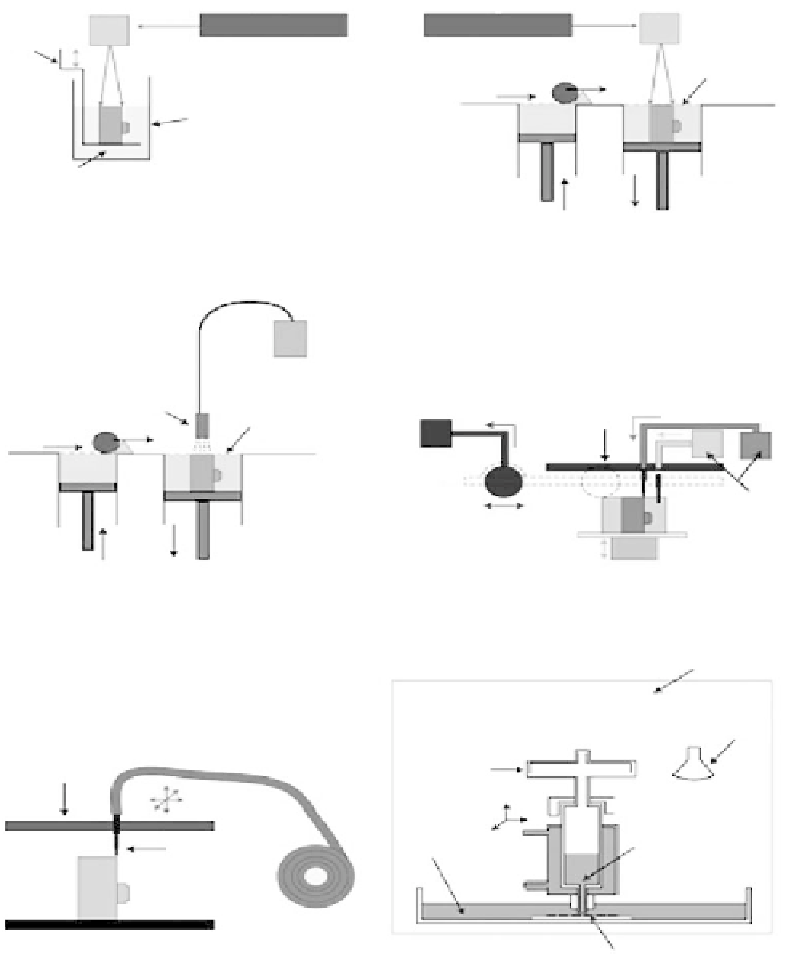
FIGURE 2.5
Schematics of SFF systems categorized by the processing technique. (A,B) Laser-based pro-
cessing systems include the stereolithography system, which photopolymerizes a liquid (A) and the SLS sys-
tems, which sinter powdered material (B). In each system, material is swept over a build platform, which is
lowered for each layer. (C,D) Printing-based systems, including 3-D printing (C) and a wax-printing machine
(D). The 3-DP prints a chemical binder onto a powder bed. The wax-based system prints two types of wax
material in sequence. (E,F) Nozzle-based systems. The fused deposition modeler prints a thin fi lament of
material that is heated through a nozzle (E). The bioplotter prints material that is processed either thermally
or chemically. (From Hollister, S.J.,
Nat. Mater
. 4, 518-524, 2005. With permission from
Nature
.)