Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
(c)
FIGURE 21.1
Schematic representation of three main types of cartilage: (a) elastic cartilage, (b) fi brocarti-
lage, and (c) hyaline cartilage.
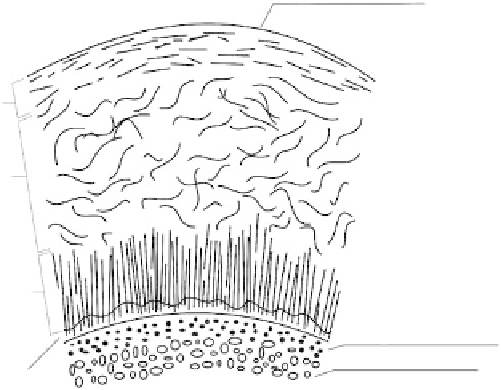
Articular cartilage
Zone I (superficial)
(10
−
20%)
Zone II (transitional)
(40
−
60%)
Zone III (deep)
(30%)
Subchondral bone
Cancellous bone
Subchondral bone
Cancellous bone
Zone IV
(calcified cartilage)
FIGURE 21.2
Articular cartilage (AC) architecture.
of cartilage in compression [2]. The liquid phase of the AC is mainly composed of water. Water
makes up to 80% of the wet weight of AC [3]. Exudation and the movement of water through carti-
lage are dominant mechanisms controlling the compressibility of the tissue. When the cartilage is
compressed, water moves aside, its thickness decreases, and the fl uid leaks out of the matrix. Water
keeps moving until an equilibrium pressure is obtained. When the loading is removed, water is
drawn back into the cartilage. Working in a hydraulic fashion, the interstitial fl uid can fl ow under
compression within the cartilage and when the load is removed the fl uid returns. Although AC lacks
a network of capillaries to convey blood, it is instead nourished by the fl ow of synovial fl uid.
From another point of view, AC is structurally graded, multilayered tissue with a fi ber-reinforced
composite structure. It is divided into four zones. Listing them from the articular surface (Figure
21.2), one can distinguish the (i) superfi cial zone, (ii) transitional (middle) zone, (iii) deep (radial)
zone, and (iv) calcifi ed cartilage zone. Each of them differs in chondrocytes arrangements, functions,
and properties. Zone 1 is thin (10% of a total AC thickness) and contains fl attened, horizontally dis-
tributed chondrocytes. Zone 2 is thicker (40-60% of a total thickness) and contains spherical chon-
drocytes. Collagen fi brils are horizontally arranged within zone 1, while in zone 2 they are randomly
distributed. Zone 3 is characterized by columnar arrangement of spheroidal chondrocytes and vertical
orientation of collagen fi brils (perpendicular to the joint surface). Zone 4 provides a direct fi xation
between the AC and the underlying subchondral bone. It contains smaller chondrocytes of lower level
of metabolic activity (cells are surrounded by calcifi ed extracellular matrix) [4].