Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
HMWK
Prekallikrein
Kallikrein
FXII
FXIIa
FX
FXI
FXIa
HMWK
FIX
FLXa
Ca
2+
PL
FVIIIa
−
Protein C
APC
FXa
FVIII
Thrombin
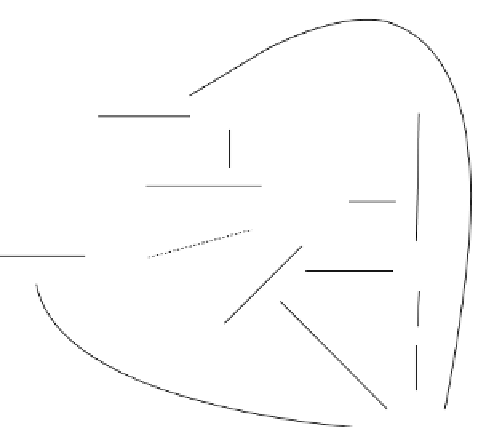
FIGURE 17.6
Intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. HMWK, high-molecular-weight kininogen; F, factor;
PC, protein C; APC, activated protein C.
Tissue damage
TF
TF.FVIIa
Ca
2+
TF.FVII
−
FVII
TFPI
FIXa
FX
FXa
PL, Ca
2+
Thrombin
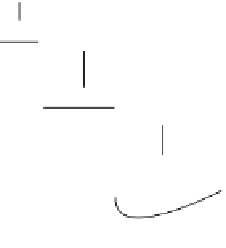
FIGURE 17.7
Extrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. TF, tissue factor; TFPI, tissue factor pathway inhibitor;
PL, phospholipids.
and so the feedback upregulation is probably the most important mechanism of TF.FVII activation.
The TF.FVIIa complex is also known as the extrinsic tenase complex. This means that the complex
can activate FX to FXa. This will result eventually in the formation of thrombin and a blood clot, as
described in the common pathway section (Figure 17.7). The TF.FVIIa complex is rapidly and effi -
ciently inhibited by the tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI).
47
Therefore, it is speculated that the
extrinsic pathway is mainly involved in triggering of coagulation and that via feedback upregulation
of the intrinsic pathway the burst of thrombin and thrombus formation are achieved.