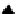Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Potentiostat
WE
REF
CE
Deposited
polypyrrole
Pyrrole + electrolyte (aq.)
FIGURE 13.3
Experimental setup: WE, working electrode; REF, reference electrode; CE, counter elec-
trode; deposited polypyrrole is shown in black covering the working electrode.
200
Oxidation peak
150
100
50
0
−
50
−
100
Reduction peak
−
150
0.6
0.4
−
1.2
−
1.0
−
0.8
−
−
−
0.2
0.0
0.2
Voltage (V)
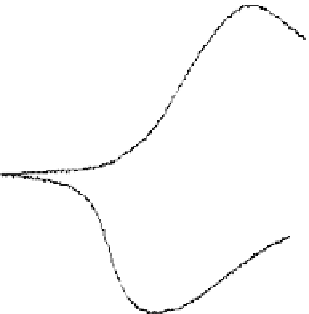
FIGURE 13.4
Cyclic voltammogram of PPy(DBS) in 0.1 M NaDBS electrolyte at 50 mV/s voltage scan.
neutrality is preserved by the movement of sodium ions from the surrounding electrolyte into the poly-
mer matrix to compensate for the negative charge of the immobile DBS
−
dopant ions. When oxidizing
voltage is applied to the polymer (0 V versus Ag/AgCl), electrons are removed from PPy, resulting in
a positively charged polymer matrix that pushes mobile sodium ions out to the surrounding solution
to preserve charge neutrality. This reaction is reversible and can be carried out by applying a voltage
ramp to the polymer while measuring the oxidizing/reducing currents, as shown in Figure 13.4.
This electrochemical method is known as cyclic voltammetry. It allows determination of the
voltages at which oxidation and reduction reactions take place. Tracing the voltammogram from 0 V
through the reduction peak to
−
1 V and back through oxidation peak to 0 V, the following events