Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(A)
SBA-15
CMK-3
(B)
Molecular dimension
of lysozyme
30
30
30
(a)
(b)
(c)
20
20
20
10
10
10
1000
0
0
1500
Specific surface area (m
2
g
−
1
)
2000
1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8
2.0
Pore diameter (nm)
4.0
6.0
Specific pore volume (cm
3
g
−
1
)
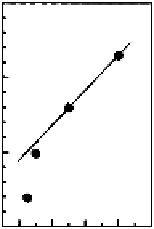
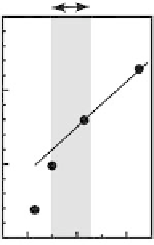
FIGURE 12.16
(A) Conceptual illustration of synthesis of CMK-3 from SBA-15. (B) Effect of structural
parameters on monolayer adsorption capacities of lysozyme onto mesoporous carbon materials: (a) specifi c
surface area, (b) specifi c pore volume, and (c) pore diameter.
media. In order to confi rm the structural stability of lysozyme after adsorption on the mesopo-
rous carbon, FT-IR spectra were recorded for the lysozyme molecules loaded mesoporous adsor-
bents CMK-3 in comparison to unloaded lysozyme. The intensity ratio between amide I and
amide II bands did not virtually alter upon adsorption of lysozyme onto the mesoporous carbon,
indicating the absence of serious denaturation accompanying changes in secondary structures
through the adsorption process. The adsorbent was also characterized by nitrogen adsorption-
desorption isotherms after the lysozyme adsorption. This investigation was to ascertain whether
the lysozyme molecule enters the mesopore of CMK-3. The amount of nitrogen adsorbed was
decreased by increasing the amount of the lysozyme adsorption. The reduction in the specifi c
mesopore volume after the lysozyme adsorption clearly indicates that the lysozyme molecules are
adsorbed inside the mesopores of CMK-3 adsorbent.
Vinu and coworkers have recently synthesized more advanced materials like novel nanocar-
bon, “carbon nanocage” [110-112], through replica synthesis using 3-D large cage-type face-
centered cubic mesoporous silica materials (KIT-5) [113], as inorganic templates. The image of
the synthesis of carbon nanocage is illustrated in Figure 12.17. It should be however noted that
these illustrations show just a rough idea of the obtained materials. The textural characteristics
of the carbon nanocage materials determined by nitrogen adsorption-desorption measurement
apparently exceed those of the conventional mesoporous carbon CMK-3. The specifi c surface area
of 1600 m
2
g
-
1
and specifi c pore volume of 2.1 cm
3
g
-
1
were obtained for carbon nanocage syn-
thesized under optimized conditions. These values are apparently larger than those reported for
conventional mesoporous carbon and CMK-3 (surface area, 1260 m
2
g
-
1
; pore volume, 1.1 cm
3
g
-
1
).
A further analysis with the method proposed by Ravikovitch et al. [114] provided the cage diameter
of 15 nm for the corresponding carbon nanocage, which has pore diameter of 5.2 nm. Integrated