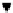Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Preparation of polymeric nano/microparticles
Monomer
Preformed polymers
Polymerization process
Polycondensation process
Physicochemical process
Mechanical process
Suspension polymerization
Emulsion polymerization
Dispersion polymerization
Precipitation polymerization
Suspension polymerization
Interfacial polymerization
Dispersion polymerization
Suspension cross-linking
Solvent evaporation
Coacervation
Extrusion
Sonication
High-speed stirring
SCHEME 7.2
Commonly employed techniques for the fabrication of polymeric nano/microparticles.
7.4.4.1
Nano/Microparticles Obtained by Polymerization of Monomers
7.4.4.1.1
Emulsion Polymerization
Emulsion polymerization is a widely used method for nanopa r ticle prepa ration. This method is classi-
fi ed into two categories based on the nature of the continuous phase in the emulsion. In the fi rst case,
the continuous phase is aqueous (o/w emulsion), whereas in the other case continuous phase is organic
(w/o emulsion). In either case, the monomer is emulsifi ed in the nonsolvent phase with surfactant mol-
ecules. The polymerization takes place in the presence of a chemical or physical initiator. The drug
to be encapsulated may be incorporated in the reaction medium during the polymerization or can be
subsequently added to the preformed particles. The advantage of this technique is that nanoparticles
with smaller size (50-200 nm) can be obtained by this technique. Nanospheres of polymethylmeth-
acrylate, poly(alkyl cyanoacrylate), polyacrylamide, etc., can be prepared by this technique.
7.4.4.1.2
Precipitation and Dispersion Polymerization
In precipitation polymerization technique, the monomer is completely miscible in the polymerization
medium, but the medium is a precipitate for the resultant polymer. The polymerization medium will
be a homogeneous reaction medium, but the polymerization will lead to the formation of a visible
precipitate. Dispersion is similar to the precipitation polymerization, but the addition of one or more
stabilizers to the polymerization medium leads to the formation of monodispersed particles.
Donini et al. reported the preparation of poly(methacrylic acid-
g
-polyethylene glycol) nano-
spheres by solution or precipitation polymerization [134]. The free radical polymerization of