Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
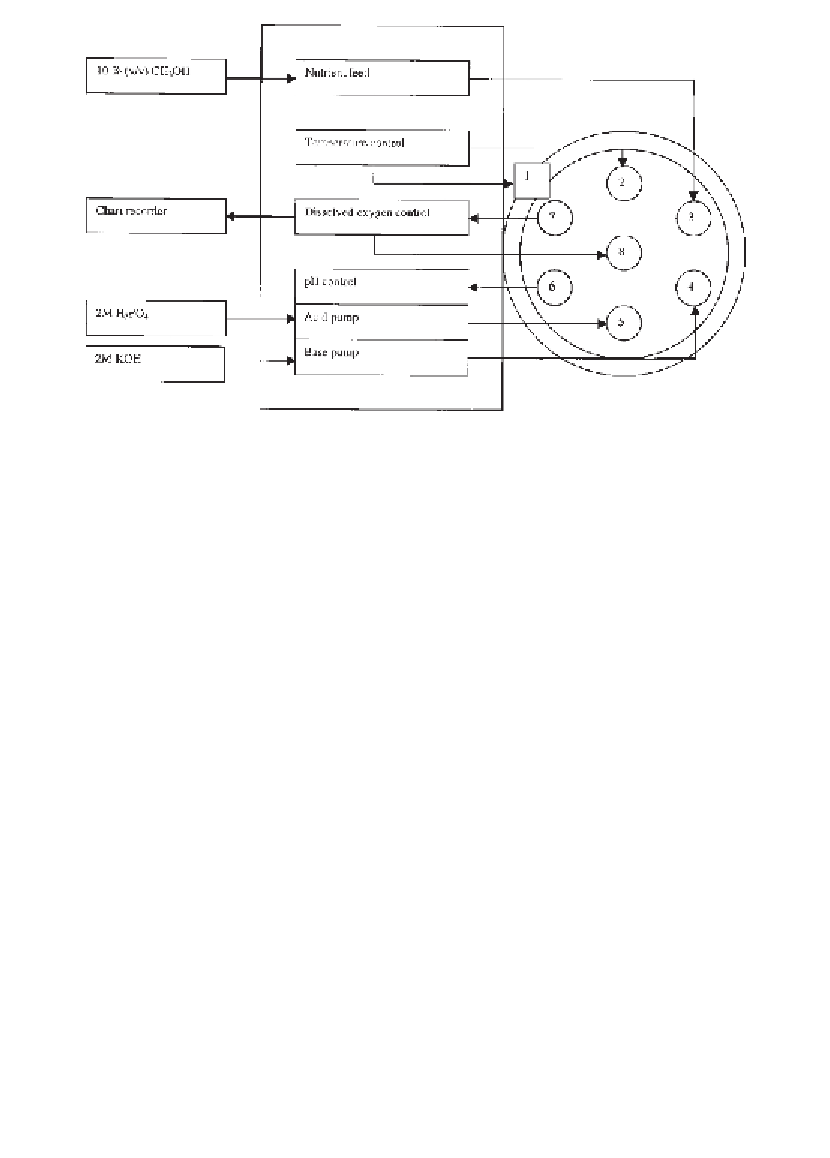
Fig. 2. Schematic representation of the fermentation vessel and controller. (1) tem-
perature-controlled jacket; (2) temperature probe; (3) nutrient-feed port; (4) base-con-
trol port; (5) acid-control port; (6) pH probe; (7) dO
2
probe; (8) impeller.
5.
D-glucose solution: Prepare a 20 % (w/v) solution in water. Filter sterilize and
store at room temperature for up to 1 yr. Use U-[
13
C]-glucose as necessary (
see
Note 3
).
6.
Antifoam solution: Autoclave polypropylene glycol 1025 and store at room tem-
perature indefinitely (
see
Note 4
).
7.
Acid control solution: Prepare and autoclave 2
M
orthophosphoric acid (corro-
sive) and store at room temperature indefinitely.
8.
Base control solution: Prepare and autoclave 2
M
potassium hydroxide (corro-
sive) and store at room temperature indefinitely.
2.3. Fermentation of P. pastoris
Methanol feed solution: Prepare fresh and filter sterilize 10% (v/v) metha-
nol (toxic) in water.
2.4. Processing of Culture Supernatants
1.
Citrate equilibration buffer pH 3.0 (per liter): Dissolve 3.15 g citric acid, 0.90 g
trisodium citrate dihydrate, and 0.20 g sodium azide (highly toxic) in water.
2.
Citrate wash buffer pH 5.0 (per liter): Dissolve 1.34 g citric acid, 3.82 g triso-
dium citrate dihydrate, and 0.20 g sodium azide (highly toxic) in water.
3.
Citrate elution buffer pH 5.0 (per liter): Dissolve 1.34 g citric acid, 3.82 g triso-
dium citrate dihydrate, 58.44 g sodium chloride, and 0.20 g sodium azide (highly
toxic) in water.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search